Software quality plays a critical role in how users experience digital products and how businesses maintain trust in competitive markets. As software systems grow more complex and release cycles become shorter, ensuring consistent quality has become a core requirement rather than an optional step.
Quality assurance (QA) provides the structure and discipline needed to maintain reliability, performance, and security throughout the development process. Instead of focusing only on finding defects, modern QA emphasizes building quality into every stage of the development lifecycle through well-defined processes and collaboration.
In this article, we explore QA best practices that help teams improve efficiency, reduce risk, and deliver high-quality software consistently. Read along to understand how strategic QA approaches, testing methods, and tools contribute to sustainable software success.
Introduction
Quality assurance is not something that happens at the end of a project. It is a continuous foundation of the software development process that supports every stage of product creation. A strong QA practice begins early and continues through planning, development, testing, and release, ensuring quality is built in and not added later.
When teams focus on quality from the start, they reduce risks, avoid expensive rework, and prevent delays caused by late defect discovery. Early QA testing helps identify issues before they grow into larger problems, saving both time and cost while improving overall product stability.
Today, quality assurance plays a strategic role in successful software delivery. QA professionals work closely with developers and product teams to align quality goals with business objectives. This approach positions QA as a key driver of reliable, scalable, and user-focused software throughout the entire lifecycle.
A visual understanding of quality assurance in the testing process (Triad)
What Is QA Testing?
QA testing is the process of evaluating software to ensure it meets defined quality standards and works as expected. It is a core part of the QA process that helps teams deliver quality software throughout the software development cycle.
QA plays a critical role in product reliability, usability, and release success. By identifying defects early, QA reduces the need for late bug fixes, supports stable releases, and ensures the product performs well for real users. Strong and continuous software testing allows teams to improve quality at every stage.
What is QA testing?
QA testing is the process of evaluating software to ensure it meets quality standards, functions correctly, and delivers a reliable user experience throughout the software development lifecycle.
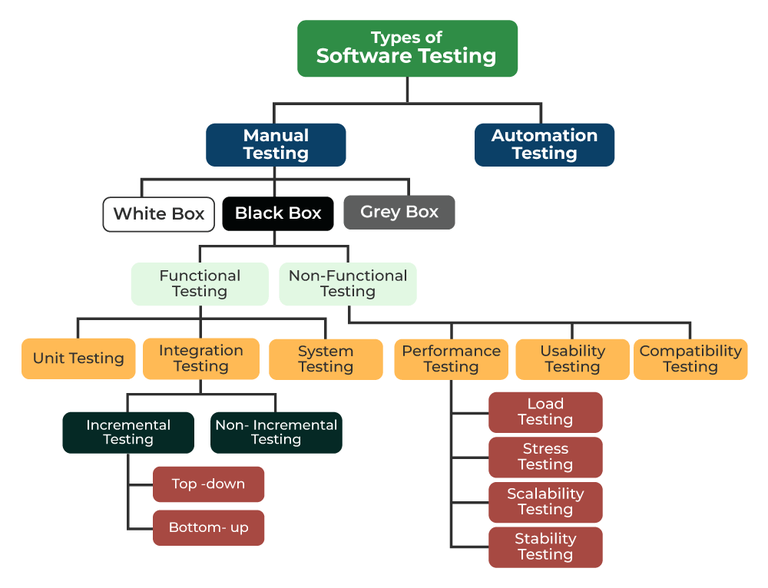
A basic overview of the key types of QA testing (GeeksforGeeks)
Below is a list of key QA testing types that you must know about:
- Unit testing: Unit tests ensure individual components or functions work correctly
- Functional testing: Verifies that features behave as per specified requirements
- Integration testing: Checks how different modules work together as a system
- Regression testing: Ensures new changes do not break existing functionality
- Performance testing: Evaluates speed, responsiveness, and stability under load
- Security testing: Identifies vulnerabilities and protects the system from threats
- Usability testing: Assesses ease of use and overall user experience
- Automated testing: Uses tools to execute repetitive tests efficiently
- Manual testing: Involves human validation for exploratory and UX-focused testing
- End-to-end testing: Validates complete user workflows from start to finish
- Box testing: Based on the tester’s knowledge of the internal system
Box testing has three main types:
- Black box testing: The tester does not know the internal system and tests it based on inputs and expected outputs
- White box testing: The tester has full visibility into the internal code, structure, and logic to validate paths, conditions, and code flow
- Gray box testing: A hybrid approach where the tester has partial knowledge of the internal system
Core QA Fundamentals
Strong software quality assurance starts with clear fundamentals that embed quality from the very beginning of development. Instead of waiting to find issues at the end, effective QA focuses on preventing defects early. This proactive approach reduces rework, lowers costs, and supports long-term product stability. Well-defined and consistent methodologies help QA teams maintain quality across every phase.
Start testing early (shift-left testing)
Shift-left testing means involving QA during planning and design, and not after development begins. When QA testing starts early, teams can review requirements, validate test cases, and identify risks before coding starts.
Early testing reduces rework by catching issues when they are easier to fix. It also accelerates delivery by preventing late-stage surprises and supporting smoother development cycles.
Balance manual and automated testing
Automation works best for repetitive tasks, regression checks, and high-volume scenarios. Automated tests improve speed and consistency, especially when supported by strong test automation frameworks and reusable test case designs.
Manual testing is essential for validating the user interface, exploring edge cases, and assessing real user behavior. The strongest QA strategies rely on manual and automated testing together. This balance ensures coverage, accuracy, and adaptability across different testing needs.
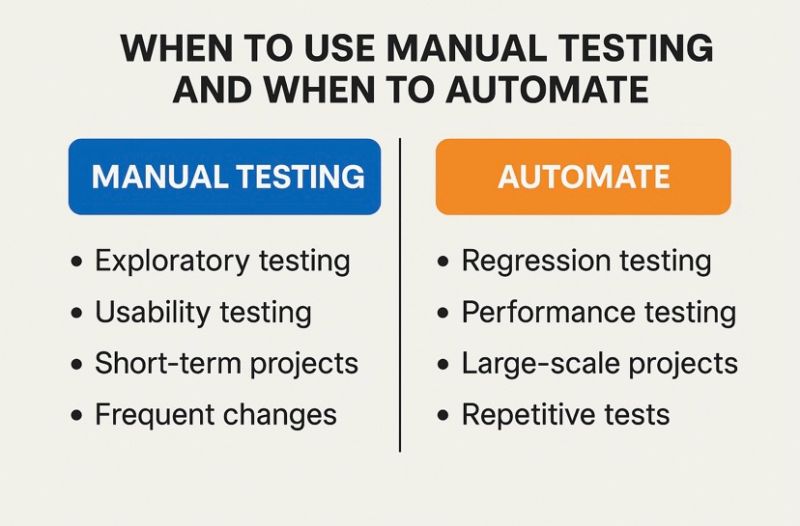
Understanding the uses of manual and automated testing (https://media.licdn.com/dms/image/v2/D5622AQFmSLsgcU4akg/feedshare-shrink_800/B56ZbZgCqBHUAo-/0/1747405779023?e=2147483647&v=beta&t=5g2-zORP5tFrAuR9OceAqxF9A1lw77sXs7UtBVlX_i4)
Integrate QA into CI/CD pipelines
Modern QA integrates directly into CI/CD pipelines, where automated testing occurs at every build and deployment stage. This setup supports continuous testing and helps teams detect issues as soon as changes are introduced.
CI/CD integration tests ensure consistent quality and faster releases. Continuous feedback loops allow QA testers and developers to respond quickly, improve test cases, and maintain high standards throughout the development lifecycle.
Strong core QA fundamentals ensure that quality is built into the product from the start. Thus, teams can deliver reliable software faster and with confidence.
QA Best Practices for Modern Development Teams
Structured QA best practices help teams improve efficiency while delivering a high quality and reliable product. Clear quality assurance best practices reduce confusion, minimize rework, and support faster releases. In modern workflows, adaptability and collaboration are essential, as QA testing must align closely with development and product goals to maintain software quality.
Let’s review some QA best practices that quality assurance teams must consider when navigating modern software development systems.
Combine automation with manual testing
Manual and automated testing play complementary roles within an effective testing strategy. Automation is best suited for repetitive tasks, regression testing, and validating new features during frequent deployments. It improves speed, consistency, and overall test execution.
Manual testing remains essential for evaluating usability, exploring edge cases, and validating real user behavior. Testing the product from the perspective of end users ensures functionality, clarity, and a smooth experience. A balanced approach using both methodologies strengthens testing practices and improves overall results.
Apply agile & iterative QA methods
In Agile environments, QA is actively involved in sprint planning, daily standups, backlog refinement, and retrospectives. This early involvement allows QA teams to clarify requirements, prepare tests in advance, and align testing goals with sprint objectives.
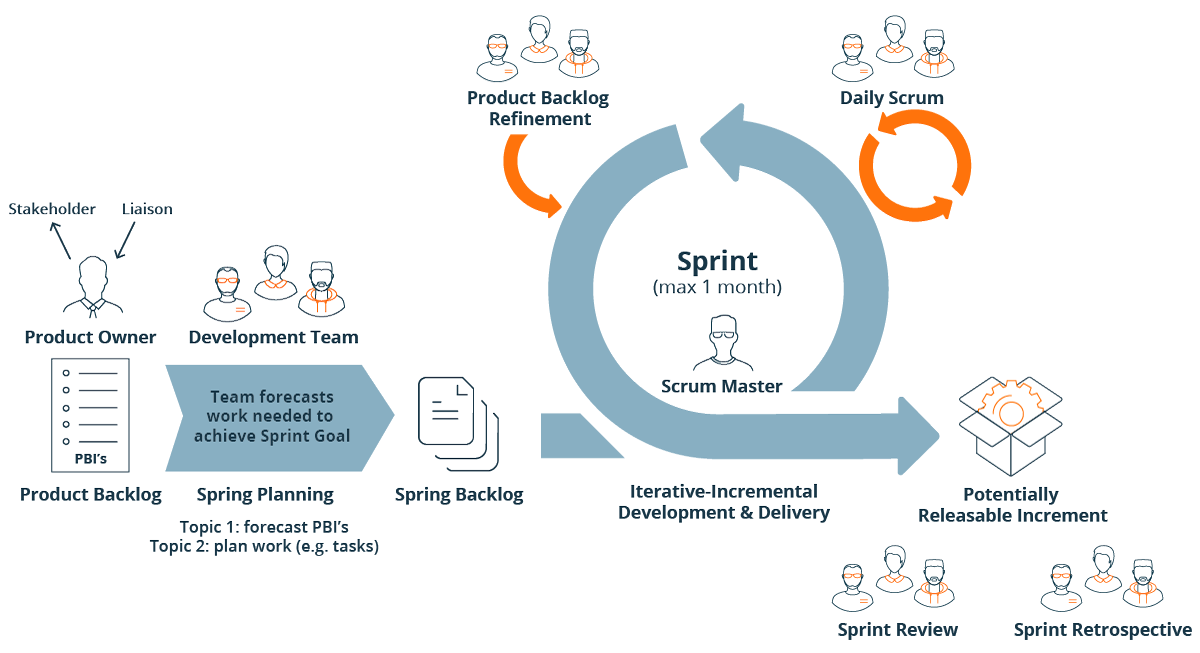
Agile methodology at a glance (SmartBear)
Iterative QA testing supports rapid feedback and continuous improvement. By testing in short cycles, teams can identify issues early, adapt quickly, and refine the testing process with each release.
Create clear, reusable, traceable test cases
Clear and consistent documentation is a key element of QA testing best practices. Test cases should follow defined standards and use simple, unambiguous language to ensure accuracy and repeatability.
Reusable and traceable test cases improve efficiency and maintain strong test coverage. Linking test cases to requirements makes it easier to track progress, identify gaps, and ensure alignment with business needs.
Test integration & end-to-end scenarios
Integration tests validate how individual components interact within the system. These tests help identify issues that may not appear during isolated testing but can impact overall functionality.
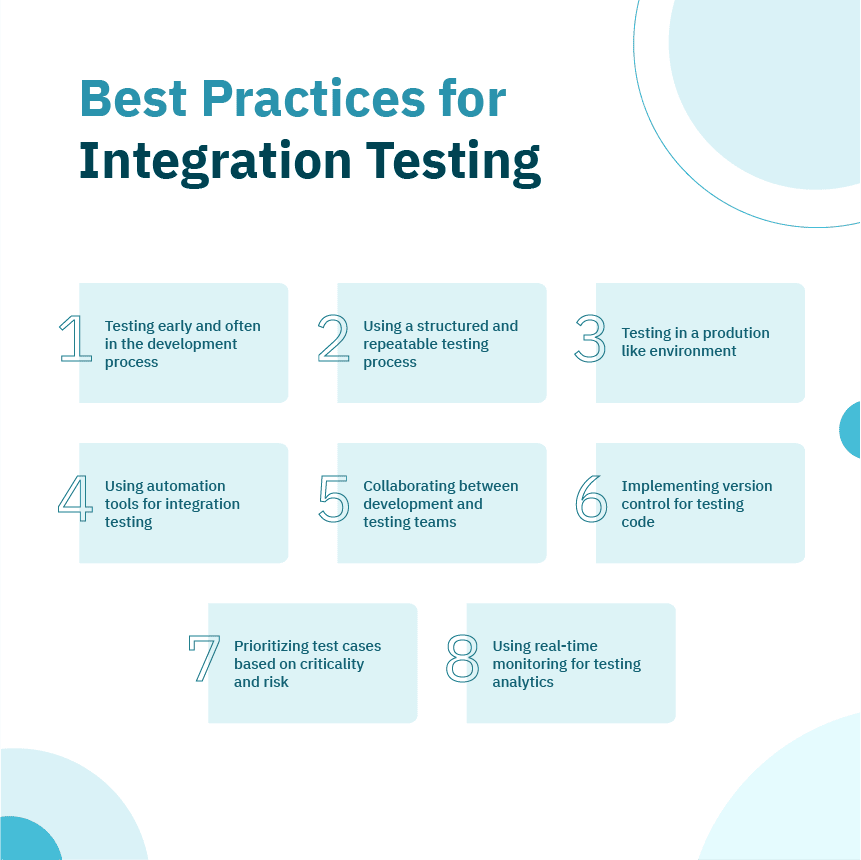
Best practices for integration testing (Opkey)
End-to-end testing verifies complete user workflows across the application. By simulating real-world usage, E2E tests prevent system-level failures and ensure the product performs reliably in production environments.
Strengthen team communication & documentation
Effective QA depends on strong communication between quality assurance, development, and product teams. Regular collaboration ensures shared understanding of goals, priorities, and risks throughout the project lifecycle.
Documentation, such as test reports and change logs, supports knowledge transfer and continuity. Clear documentation helps teams maintain software quality even as team members or requirements change.
Prioritize security & compliance testing
Security and compliance are essential parts of modern QA best practices. Following standards such as the Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP) helps teams identify vulnerabilities and protect sensitive data.
Compliance testing ensures the product meets regulatory and data protection requirements. These practices reduce risk, prevent costly issues, and reinforce trust in the final release.
Use modern, scalable QA tools
Selecting the right tools is critical to an effective testing strategy and QA methodology. Tool choices should align with project size, technology stack, and automation goals to support long-term scalability.
Tools such as Selenium, Cypress, Katalon, and Playwright enable efficient testing and integration with modern workflows. They help teams apply best practices consistently while supporting growth and complexity.
Perform continuous & regression testing
Continuous testing allows teams to validate changes as they are introduced, reducing the chance of defects reaching production. It supports faster feedback and more confident releases.
Regression testing ensures that existing functionality remains stable when updates are made. Maintaining strong regression suites is essential for protecting core features and preserving quality standards.
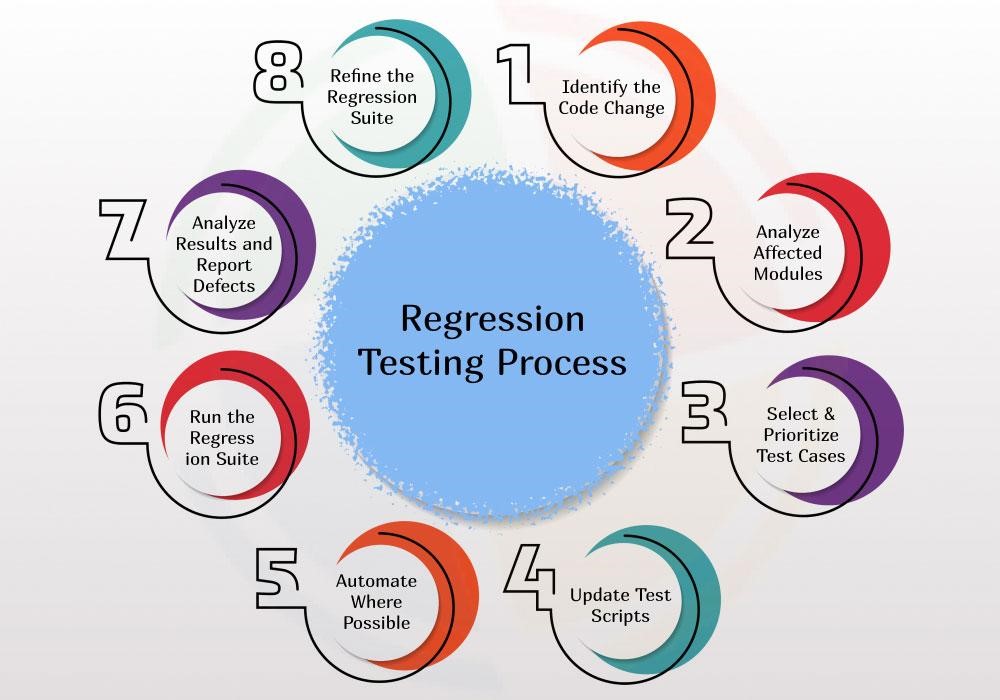
Understanding regression testing process (Aegis Softtech)
Measure, analyze & improve test coverage
Measuring test coverage provides insight into how thoroughly the product has been tested. Coverage data helps teams improve testing focus and resource allocation. Common KPIs such as pass rate, defect density, and automation rate support teams to make informed decisions. These metrics drive continuous improvement in the test execution and overall software quality.
Adopting these structured QA best practices enables teams to deliver reliable, high-performing software with confidence. It enables teams to consistently meet quality standards and always deliver a quality product that scales with business needs.
Choosing the Right QA Tools
Selecting the right QA tools has a direct impact on testing speed, accuracy, and scalability. The tools a team uses influence how quickly they can validate new features, identify potential issues, and deliver quality software. An effective toolset supports proven QA testing best practices and aligns with the team’s methodology, technical skills, and overall workflow.
QA tools should be chosen based on supported programming languages, team experience, and how well they fit into the existing testing environment. The right tools also complement different testing approaches and help teams apply consistent methodologies across projects.
What are the key aspects to consider when choosing a QA tool?
Below are the key aspects to consider for a suitable QA tool selection:
- Project testing requirements
- Technology stack compatibility
- Automation support and ease of use
- Learning curve
- CI/CD integration
- Scalability
- Cross-browser and cross-platform support
- Reporting and analytics
- Community and vendor support
- Cost and licensing
- Security and compliance support
- Integration with existing tools
How modern tools streamline QA workflows?
Modern QA tools support automation, seamless integration, and detailed reporting. These capabilities reduce manual effort and improve test reliability across the development lifecycle.
CI/CD compatibility allows tests to run automatically with every build and deployment. This integration supports faster feedback, quicker releases, and consistent quality checks as new features are introduced. As a result, QA teams can focus more on risk analysis and less on repetitive tasks.
Recommended QA platforms & environments
Below are commonly used QA platforms, along with their primary use cases and supported ecosystems:
Selenium
Selenium is one of the most widely used tools for web application test automation. It allows QA teams to write automated tests that simulate real user actions across different browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, and Edge.
It supports multiple programming languages, including Java, Python, C#, and JavaScript, making it flexible for diverse teams. Selenium is ideal for large projects that require extensive cross-browser testing.
Cypress
Cypress is designed specifically for modern web applications built with JavaScript frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue. It runs directly in the browser, which makes test execution fast and debugging easier.
Because Cypress works closely with frontend code, it is well-suited for UI and component testing. However, it is limited to JavaScript and primarily supports Chromium-based browsers.
Playwright
Playwright is a powerful end-to-end testing tool that supports Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit browsers. It provides reliable test execution and handles modern web features such as dynamic content and single-page applications.
Playwright supports JavaScript, Python, and Java, making it accessible to both frontend and backend-focused teams. It is ideal for stable UI testing and full user journey validation.
Katalon
Katalon is an all-in-one testing platform that supports web, API, and mobile testing within a single interface. It offers built-in keywords, reporting, and test management features, reducing setup time.
The platform supports multiple scripting options and is suitable for teams that want to start testing quickly without heavy configuration. It works well for small to mid-sized teams.
Jenkins
Jenkins is not a testing tool itself but a CI/CD automation server that runs tests automatically during builds and deployments. It integrates with tools like Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright.
It is language-agnostic and helps teams implement continuous testing as part of their delivery pipeline. It ensures tests run consistently whenever new code is pushed.
Below is a comparison table for a quick overview of these QA platforms and environments.
| Tool | Primary use case | Supported languages | Ideal scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selenium | Web automation | Java, Python, C#, JS | Cross-browser testing |
| Cypress | UI testing | JavaScript | Modern frontend apps |
| Playwright | End-to-end testing | JS, Python, Java | Stable UI workflows |
| Katalon | Unified testing | Multiple | Low setup effort |
| Jenkins | CI/CD automation | Language-agnostic | Continuous testing |
Choosing the right QA tools enables teams to test faster, scale efficiently, and maintain consistent quality. When tools align with team workflows and testing approaches, they help deliver quality software where a product meets goals and expectations.
Conclusion
Quality cannot be treated as a final step in the development process. It must be built into every phase, from planning and design to testing and release. When quality assurance is embedded throughout the process, teams can detect issues early, reduce rework, and maintain consistent quality as products evolve.
Continuous QA plays a critical role in delivering stable, secure, and user-focused software. Ongoing testing, clear standards, and regular feedback help ensure that each update meets both technical and user expectations without slowing delivery.
Rather than viewing QA as a checkbox, organizations should treat it as a strategic investment that drives long-term success. To take action, teams should review their current QA workflows, adopt structured QA best practices, and invest in tools and processes that support continuous improvement and sustainable product quality.
Feb 5, 2026
