The field of UX design and research is advancing at a rapid pace. With the introduction of new technologies, designers are exploring new ways to work more efficiently. One such area is the application of artificial intelligence (AI) in design, particularly in usability testing.
AI usability testing leverages machine learning (ML) and automation to evaluate the design of products and services. Instead of relying solely on manual observation and traditional methods, AI helps analyze interaction patterns and highlight usability issues in real-time.
With the help of AI, designers can strengthen modern usability tests in several ways. The power of AI tools and the capability to process thousands of events enable design teams to gather better insights in a much shorter time.
For teams working with a UX design agency, AI-driven analysis enhances research workflows and helps deliver stronger, more evidence-based UX improvements for complex digital products.
In this article, we introduce the concept of AI usability testing while focusing on the utility of AI and ML in UX design. We also mention some important tools and the steps to conduct effective usability tests with AI.
Join us as we explore this exciting new topic that can significantly enhance your design workflow.
Defining AI Usability Testing
AI-driven usability testing is a fairly modern approach to user testing where design teams use machine learning to observe how people interact with digital products and services. For leaders weighing whether to build this capability in-house or collaborate with external specialists, comparing what top UX design agencies typically deliver can help set a realistic benchmark for rigor, tooling, and operating cadence. Instead of relying only on manual reviews, teams use AI to gather behavioral insights across the entire user experience.
What is AI usability testing?
AI usability testing refers to the use of artificial intelligence to enhance traditional approaches to usability testing. Researchers use AI tools and best practices to gather valuable insights, leading to data-driven decisions.
AI adds value to the process by focusing on all the important aspects necessary for an effective user test. With the help of AI, designers can track clicks, identify scroll depth, map navigation paths, and highlight pain points. These insights can then be interpreted and analyzed in a faster, automated manner to reveal friction points and UX patterns. By automating the process to some extent, testing can become more consistent and objective.
The real value of AI is not just the speed, but also the value that automated analysis brings. AI can detect trends, group similar behaviors, and highlight recurring issues faster and better than traditional methods. This transforms UX insights by reducing manual effort and enriching the overall testing process.
Why Usability Testing Matters?
Usability testing is a critical part of the entire design process. Whether it is a physical product, a mobile application, or a digital service, usability testing brings user feedback and pain points to light, which can then be used to create better iterations of any design.
Usability testing is essential because intuitive, well-structured UX directly impacts business outcomes. Clear, interactive interfaces reduce cognitive load, help users complete tasks quickly, and create positive perceptions of a product. Strong methods for evaluation, therefore, ensure that teams catch users’ pain points early and comprehensively.
When organizations overlook usability tests, the risks grow quickly. Higher abandonment, lower conversions, and rising user frustration are common results of poor usability. Bad designs force people to work harder than they should, while effective testing keeps experiences seamless and aligned with user expectations.
How AI Enhances Usability Testing?
AI enhances usability testing by accelerating analysis, uncovering deeper behavioral patterns, and improving accuracy across UX evaluations. Teams that use AI can get results faster compared to traditional user testing. Some key ways in which AI can enhance usability testing are as follows.
AI-powered test creation and data collection
AI tools can help generate real-world test scenarios based on user journey maps, product specifications, and audience personas. This reduces the effort involved in test creation and ensures that testing covers a broad range of interactions.
When tests are being conducted, AI tools and systems can help capture data, such as clicks, success and failure rates, and user journeys, without requiring extensive human oversight. By automating data collection, teams significantly reduce manual work and gather more consistent inputs for UX decision-making.
AI behavioral and interaction analysis
Using AI tools, designers can analyze interactions, including clicks, heatmaps, and multi-step navigation paths. These patterns reveal what users actually do when they interact with a product or service. By processing large volumes of data efficiently, AI uncovers insights that traditional methods might overlook.
Since AI can detect hesitation, repeated attempts, and abrupt backtracking, it highlights exactly where confusion or friction occurs. These insights help teams validate assumptions, refine user flows, and improve the overall user testing process with greater accuracy.
Predictive UX insights with machine learning
AI can leverage the power of machine learning models. These models can help recognize behavioral patterns that indicate user pain points, such as navigation loops or repeated errors. By interpreting these trends, ML models predict issues before they become complicated problems.
These predictive insights then support a more proactive approach to UX design. Design teams can prioritize changes, redesign, and interaction based on anticipated struggles, thus improving outcomes.
Real-time AI insights and feedback
AI tools can track and gather real-time data as users interact with products and services during usability testing. Some tools can also send alerts the moment unusual behaviors or anomalies appear. This immediate feedback enables teams to react more quickly to emerging issues, thereby reducing the delay between observation and action.
AI also provides instant recommendations on how to improve interactive elements in design and refine the layout. By surfacing insights during user testing, AI tools reduce the wait time typically associated with manual reviews.
Core Components of AI Usability Testing
AI usability testing relies on several core elements for the successful design, development, and analysis of usability testing. Some important technologies, such as machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing, allow designers to interpret behavior and improve UX insights.
What are the core components of AI usability testing?
The core components of AI usability testing are as follows.
- NLP for user feedback analysis
- Eye tracking and emotion recognition
- AI heatmaps, click patterns, and navigation flow
- Automated video and screen recording analysis
The core elements involved in conducting quality AI usability testing are discussed below.
NLP for user feedback analysis
Natural language processing (NLP) helps analyze large volumes of content from surveys and open-ended user responses. Instead of manually reading every comment from users, NLP automatically extracts sentiments, recurring themes, and pain points.
NLP not only summarizes feedback but also highlights emotional elements, providing a clearer view of what users value or struggle with. This structured understanding enriches UX insights and makes usability tests more actionable, particularly when dealing with multilingual or high-volume datasets.
Eye tracking and emotion recognition
Along with NLP, AI-powered eye tracking tools reveal where users focus during an interaction and how much time they spend on specific design elements. These insights highlight whether layouts guide attention effectively or cause confusion.
Emotion recognition adds another layer to the analysis by detecting frustration, delight, or hesitation through facial cues, changes in voice, and expressions. Together, these signals help teams understand cognitive load and emotional reactions that traditional user testing might miss.
AI heatmaps, click patterns, and navigation flow
AI can also enhance the collection and analysis of both quantitative and qualitative data, such as heatmaps, click patterns, and navigation flow. AI-powered heatmaps visualize high-attention areas, showing which elements attract the most engagement. Similarly, click-pattern analysis highlights where interactions succeed or fail, and navigation flow maps illustrate how users move in a step-by-step manner.
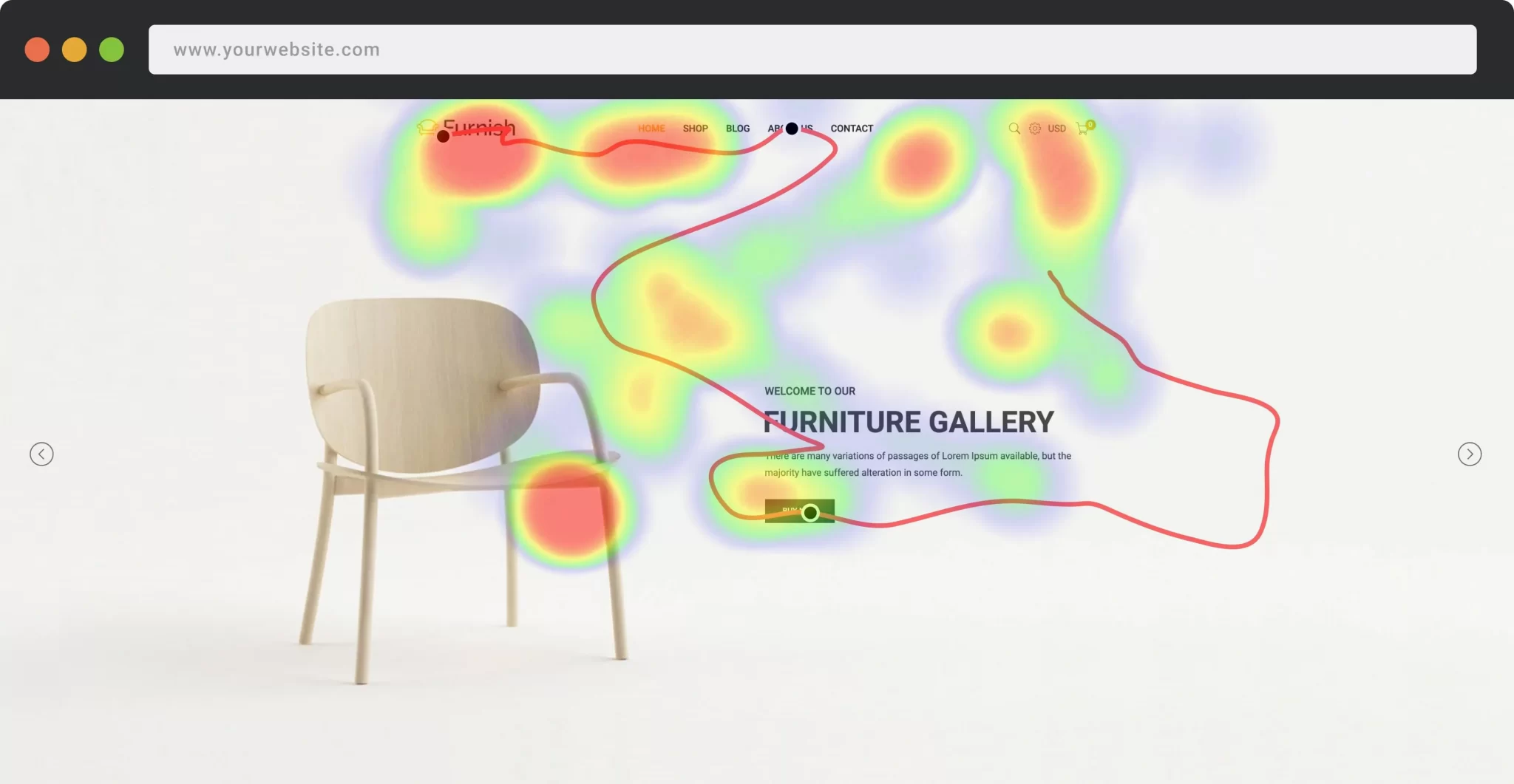
Heatmaps and Click Patterns (Image Source)
As AI can process thousands of sessions quickly, the insights gathered from these visual models are more accurate and enriching as compared to manual user testing. They help teams identify pain points, optimize layout structure, and support clearer decisions during UX research.
Automated video and screen recording analysis
Traditional review of usability testing sessions requires teams to watch all recordings manually. This is quite a time-consuming and demanding task. AI removes this barrier by scanning large volumes of video and screen capture at a much faster rate to identify key interaction moments, hesitation points, and errors.
This efficiency in data analysis frees up the time for design teams, which they can then invest in interpreting insights rather than sifting through hours of footage. By highlighting key interaction moments, AI strengthens the efficiency and depth of usability tests, thus producing richer, more focused UX recommendations.
Benefits of AI in UX Testing
The introduction and incorporation of AI in usability testing bring significant advantages to UX research. On the one hand, AI accelerates testing and saves time. On the other hand, it improves accuracy and uncovers deeper behavioral patterns.
What are the key benefits of AI in UX testing?
Some important benefits of AI in UX testing are as follows.
- Faster testing and lower research costs
- Objective, data-driven decision-making
- Better accessibility and inclusion analysis
- Scalable continuous UX optimization
Faster testing and lower research costs
AI dramatically reduces the time required to gather and analyze data in usability testing. Processes that can take days and weeks in manual user tests can be completed in minutes when using AI.
Reduced time directly impacts the utilization of resources. Organizations can now run more studies with fewer resources, enabling broader user testing coverage.
Objective, data-driven decision-making
AI brings an objective approach to the interpretation of results. By focusing more on measurable behavioral insights, AI reduces subjectivity and brings more consistency to data analysis. This perspective can significantly strengthen strategic UX decisions.
If applied appropriately, AI can also remove biases and emotional influence, thus ensuring that the recommendations are rooted in real data. This creates a more reliable decision-making process, especially when dealing with competing product concepts.
Better accessibility and inclusion analysis
AI tools can also improve the accessibility of any design, making products and services more inclusive. These tools can evaluate contrast, typography, and navigation, thus helping teams identify accessibility issues early. AI tools can also assess the compatibility of designs with assistive technology to ensure that the user experiences meet diverse user needs.
Accessibility and Inclusion in Design (Image Source)
Another strength of AI lies in its ability to create and simulate scenarios. Designers can test interfaces for low vision, color blindness, and motor limitations to reveal and understand issues at a much deeper level. These capabilities improve inclusive UX design and strengthen compliance across platforms.
Scalable continuous UX optimization
An important challenge for designers is to ensure scalability and robustness in their products and services. AI supports continuous monitoring and iterative improvements by analyzing and comparing real-time behavior across different versions of a design. With this monitoring, design teams gain constant feedback, keeping products aligned with user expectations.
Additionally, AI user testing can be replicated across large user groups, thus saving designers from the complications that can arise with scalability. This approach makes testing an ongoing, adaptive process rather than a one-time event.
AI Usability Testing Tools
As AI is advancing in every field, sophisticated tools are being introduced at a rapid pace. UI/UX design is also a beneficiary of this advancement. AI usability tools enhance UX research by automating analysis, improving testing, and uncovering behavioral patterns that manual usability tests often overlook.
Some important AI usability tools are discussed below.
Hotjar
Hotjar utilizes AI-powered heatmaps and session replays to demonstrate how users interact with a design or service. Hotjar’s features highlight pain points and user journey trends, helping teams refine layouts and accelerate workflows.
FullStory
FullStory specializes in behavioral analytics, enabling designers to automatically identify anomalies and user frustrations. Its machine learning engine highlights key moments from user sessions, offering powerful insights for improving UX and reducing manual review time.
Mixpanel
Mixpanel is another important tool for AI usability testing. It provides predictive analytics and automated trend detection. The built-in AI tools in Mixpanel group behavior patterns and inform data-driven decisions.
Other helpful tools, such as Contentsquare, Smartlook, and Mouseflow, also offer AI-driven insights,
AI Usability Testing Process
AI usability testing is a strategic process that follows a structured workflow from goal-setting to tool selection, data capture, analysis, and iteration. Each step leads into the next, ensuring a process that promises actionable UX insights.
What is the step-by-step process for AI usability testing?
The steps involved in AI usability testing are as follows.
- Define goals and user scenarios
- Choose AI tools
- Collect and process UX data
- Analyze AI insights
- Implement UX improvements
Five important steps involved in AI usability testing are discussed below.
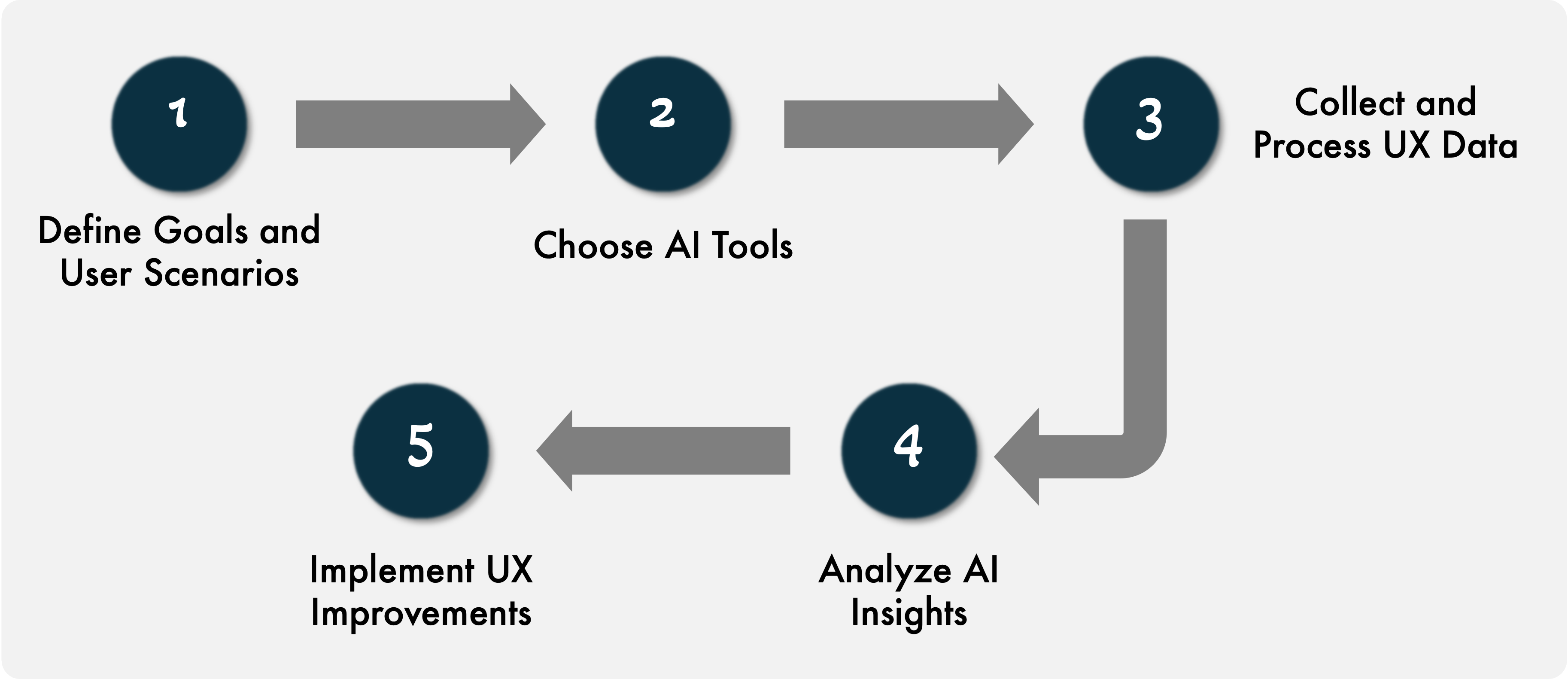
AI Usability Testing Process
AI Usability Testing Process
Step 1: Define goals and user scenarios
When conducting AI usability testing, start by identifying clear objectives and mapping critical user flows. It is also important to specify KPIs such as success rates, time on task, or error frequency to define the focus of the study.
Another important aspect of this step is to outline realistic user scenarios that mirror real-world contexts. These scenarios help structure testing and ensure the insights directly reflect users’ needs and design goals.
Step 2: choose AI tools
Once the goals and scenarios are well-defined, the next step is to select appropriate AI tools for usability testing. Designers and researchers select tools that align with the product or service's design and the type of insights required.
This is where designers consider the type of data they need to gather and analyze, such as heatmaps and sentiment analysis. Careful selection of AI tools can make the process efficient and effective.
Step 3: collect and process UX data
After selecting the tools, the usability test sessions begin. Since AI tools can automatically capture recordings, survey responses, and event logs, designers can focus on behavioral insights. Once the data is collected, AI and ML models then clean, organize, and process the data for analysis.
Step 4: analyze AI insights
AI models are particularly effective in clustering similar behaviors, detecting anomalies, and revealing friction points that users encounter throughout the experience. This process helps design teams organize insights and maximize their value.
With the help of the analysis conducted in this step, AI tools can provide design recommendations highlighting the elements that need refinement. By combining statistical results with AI-generated insights, teams gain a clearer direction for their design projects.
Step 5: implement UX improvements
The final step in the AI usability testing process involves translating the insights into specific, actionable interface updates. These could include simplifying flows, improving clarity, or adjusting the layout.
This is also the step where designers need to prioritize areas with the highest impact on user satisfaction. After making the needed changes, designers can then run another round of testing to assess the improvements. This iterative design and testing cycle enhances product quality and ensures that updates effectively address user needs.
AI Usability Testing vs. Traditional Methods
AI usability testing methods gather and analyze data at a much faster pace. With the help of AI and ML, designers can analyze thousands of interactions, highlight user pain points, and generate predictive insights to anticipate issues before they spread. These strengths make AI particularly well-suited for continuous optimization and fast-paced design ecosystems.
Traditional methods, on the other hand, offer a deeper contextual understanding that AI cannot fully replicate. Human researchers interpret motivations and emotions that shape user behavior. The perspectives of designers, therefore, provide rich, qualitative insights that cannot be extracted with AI tools.
If we compare AI usability testing and traditional user testing methods, we can say that AI provides breadth while human-driven approaches provide depth. AI highlights what is happening, and human researchers shed light on why it happens.
For designers and researchers, a hybrid approach would deliver the strongest results. When adapting this approach, teams can utilize AI to prioritize problem areas and then apply traditional testing methods to gain a deeper, human-level understanding of the issues, ultimately leading to refined solutions. Such an approach would ensure that both analytical accuracy and human-centered insight are taken into consideration during the design process.
Conclusion
AI is reshaping UX design and research on multiple levels. From data collection and analysis to predicting user behavior and designing interactive interfaces, AI can enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of UX design. The capability of AI tools to process large datasets and reveal insights instantly provides designers with a strong foundation for enhancing digital experiences.
However, AI is most effective when paired with human expertise. Designers and researchers provide the contextual understanding and reasoning that AI cannot replicate. Together, humans and AI tools form a balanced approach that blends analytical depth with human-centered interpretation.
As AI tools continue to develop rapidly, continuous, data-driven improvement will shape the future of UX design. Teams that integrate AI-powered insights with thoughtful human evaluation will adapt more quickly, design more intuitively, and deliver products that evolve in response to users’ needs.
Dec 16, 2025
