Every business depends on information to keep operations running smoothly. From customer records to sales analytics, data drives decisions and helps organizations stay competitive. However, as systems become increasingly complex, one challenge becomes increasingly common: data redundancy.
When the same data is stored across multiple locations, it can either strengthen a system’s reliability or create unnecessary complications. If you’re evaluating build partners, lists of best web app development companies can help you quickly sanity-check who has relevant experience with scalable system design. Managing this balance is key to keeping performance high and costs low.
For businesses investing in digital infrastructure or working with a web app development company, understanding and controlling data redundancy is a crucial part of building efficient and scalable systems.
In this article, we will explore data redundancy, why it matters, and how businesses can manage it effectively.
Read along to discover how innovative redundancy strategies can turn data duplication from a problem into a powerful safeguard.
Introduction
Every modern business depends on data to keep operations running and customers satisfied. From sales transactions to customer profiles, data is the backbone of daily decision-making. With so much information flowing through different systems, it is common to find multiple copies of data stored in other places. This is what we call data redundancy.
In simple terms, data redundancy means storing the same information more than once. Sometimes it is intentional, like creating backups to protect against system failures. Other times, it is unintentional, often caused by poor design or lack of coordination between systems. Either way, redundant data is now a regular part of how modern systems work.
Hence, data redundancy improves reliability, protects customer information, and ensures faster access when needed. However, if not handled well, it can also result in increased costs, slow performance, and confusion. Organizations must work to achieve an appropriate balance for efficient operations.
Data redundancy is about storting same data at multiple locations (Educate Computer)
What Is Data Redundancy in Modern Systems?
Data redundancy happens when the same data is stored in more than one place. It means keeping data across multiple systems, databases, or files. These extra copies are often called redundant data.
What is data redundancy?
Data redundancy is the practice of storing the same data in multiple locations, either intentionally for backup and security or unintentionally due to duplication errors.
There are two main reasons for data redundancy: intentional and accidental duplication.
Intentional duplication happens when businesses deliberately create duplicate records or backups. This helps protect against data loss, system failures, or corruption. In such cases, redundancy is part of a well-planned system design meant to ensure reliability.
Accidental duplication, on the other hand, results from poor database structures or weak data management. These unplanned copies often make systems more complicated to manage and can lead to confusion, corruption, or inefficiencies over time.
Understanding possible ways of data duplication (Monte Carlo Data)
Whether planned or unplanned, redundancy plays a vital role in modern systems. Managed well, it improves security, ensures better performance, and supports stronger system design, while unmanaged redundancy can quickly turn into a challenge, creating risks instead of benefits.
Types of Data Redundancy
Data redundancy can take different forms depending on how and why copies of data are created. Understanding these types helps organizations manage information more effectively and reduce unnecessary duplication.
Knowing the difference also ensures that data replication serves a purpose, like improving reliability or preventing data loss, rather than creating confusion.
Unintentional vs. intentional redundancy
Unintentional redundancy occurs by accident. It usually happens when systems lack proper structure or normalization, causing the same information to be stored in multiple locations.
For example, a customer’s email might appear in separate files for billing, support, and marketing without any link between them. Over time, this leads to inconsistencies and errors.
Intentional redundancy, on the other hand, is planned. It is a key part of data replication strategies designed to protect against data loss and system failures. For instance, cloud services often keep multiple copies of data across servers to ensure availability even if one location fails. This form of redundancy supports reliability and business continuity.
Full vs. partial data duplication
Full duplication means creating complete copies of data in multiple locations. This is useful when systems must be restored quickly after a failure, such as in backup servers or disaster recovery setups. It can also increase storage costs if not managed properly.
Partial duplication, by contrast, only replicates specific data segments that are most critical. For example, an organization might only back up customer transaction details instead of the entire database. This approach helps reduce storage needs while keeping essential information safe.
Logical vs. physical redundancy
Logical redundancy happens at the data model level. It means the same information is represented in different ways within a system. For instance, two related tables in a database might both store a customer’s ID.
Physical redundancy exists at the storage or hardware level. It involves storing identical copies of data on different physical media, like hard drives or servers. This is a standard part of data replication for backup and fault tolerance.
By classifying redundancy clearly, organizations can identify where duplication helps and where it hurts. The right balance ensures that data redundancy strengthens systems rather than creating unnecessary complexity.
When Is Data Redundancy Beneficial?
When used correctly, data redundancy can add real value to modern systems. It helps protect information, improve performance, and strengthen overall reliability.
While too much redundant data can cause problems, the right balance keeps systems stable and businesses running smoothly, even during unexpected failures. Let’s explore key instances where data redundancy is beneficial.
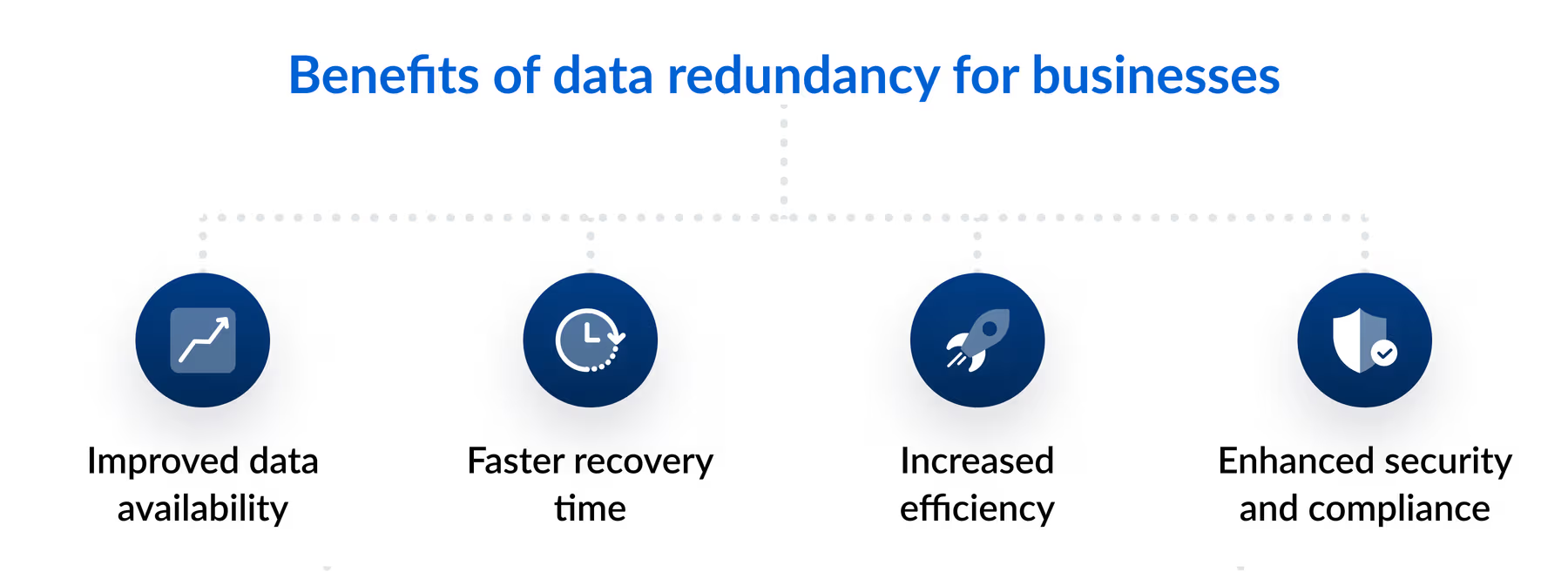
A quick glimpse of key advantages of data redundancy (Box Blog)
Enhancing reliability and fault tolerance
One of the main reasons organizations use redundant systems is to improve reliability.
By storing multiple copies of data across different servers or devices, businesses can prevent downtime when one part of the system fails. This built-in protection ensures that users still have access to critical information even if the hardware malfunctions.
For example, in a banking system, transactions are often replicated in real time to secondary servers. If the central system crashes, the backup automatically takes over, keeping services uninterrupted. This is how redundancy strengthens both hardware and system-level protection.
Improving availability and access speed
Data redundancy protects systems and speeds them up. When the same information is stored in multiple locations, users can access the nearest or least busy storage point. This reduces the database workload and speeds up data retrieval, especially in large-scale applications.
For instance, content delivery networks (CDNs) use redundant data across different regions to ensure websites load quickly for users. This approach enhances both availability and user experience.
Faster backup and disaster recovery
In disaster scenarios, redundant systems play a key role in quick recovery. Since multiple copies of data already exist, backup and disaster recovery processes become much faster. Businesses can restore operations with minimal data loss and shorter downtime.
For example, cloud service providers automatically replicate information across different data centers. If one region experiences a failure, another takes over immediately. This seamless transition shows how redundancy enables rapid reactivation.
Load distribution and scalability
Data redundancy also supports system growth and scalability. By distributing redundant data across several storage units or servers, the system can handle higher traffic without slowing down. Load is shared instead of being concentrated on one database or server.
For example, e-commerce platforms often spread customer and order information across multiple servers. This allows them to process thousands of transactions at once, ensuring smooth performance even during sales peaks.
When managed correctly, data redundancy is strategic. It keeps information secure, systems responsive, and businesses ready for growth.
Risks of Excessive Data Redundancy
While data redundancy can strengthen systems, too much of it can create serious challenges. Poorly managed redundant data increases costs, reduces performance, and complicates recovery.
What was meant to protect against a disaster can easily become a technical and financial burden if not controlled. Below are a series of situations where redundant data can become a problem.
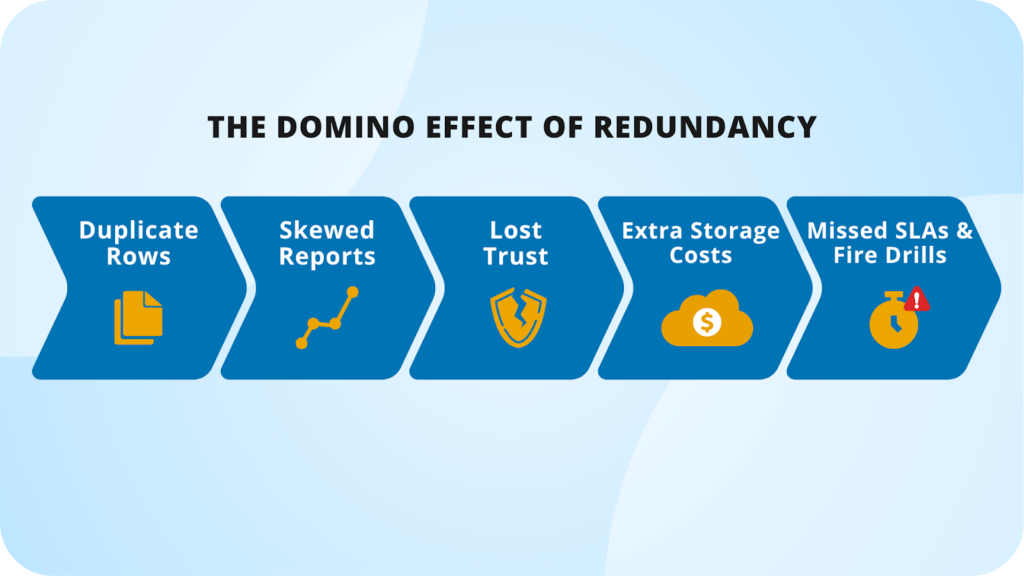
Overview of the potential impacts of excessive redundancy (Monte Carlo Data)
Data inconsistency and conflicts
When there is excessive redundancy, it becomes hard to keep everything accurate and up to date. Different versions of the same information may exist in separate systems, leading to data conflicts. For example, a customer’s phone number might be updated in one database but remain outdated in another.
These minor sync issues can cause significant confusion, mainly when systems depend on accurate records to function correctly. In some cases, incorrect or mismatched data can even affect disaster recovery, making it difficult to restore the correct version after a failure.
Increased storage costs and inefficiency
Every extra copy of data takes up space. When redundant data grows unchecked, systems require more storage capacity and computing power. This directly increases operational costs. Businesses may end up paying for massive copies of data that serve little to no purpose.
Like keeping full backups of every system version without removing outdated ones can quickly fill up storage servers. This wastes resources that could be used for more critical disaster recovery or system optimization.
Performance bottlenecks and sync issues
Too much data redundancy can also slow down systems. Synchronizing redundancy across multiple locations takes time and computing effort. When sync processes lag, users experience delays, errors, or incomplete updates.
For instance, if an e-commerce platform’s product data is not appropriately synced between servers, customers might see outdated prices or unavailable items. These performance issues not only frustrate users but also hurt business credibility.
While redundancy protects data during a disaster, excessive or poorly managed duplication does the opposite, reducing efficiency and increasing costs. Finding the right balance between safety and simplicity is key to keeping systems healthy and reliable.
Data Redundancy in Cloud Computing
In cloud computing, data redundancy is more than just a backup plan. It is a built-in strategy for stability and trust. Cloud platforms use redundancy to ensure that users never lose access to their files, even if one part of the system fails.
The role of data replication
Modern cloud systems rely on distributed storage to keep data safe. This means that copies of the same information are stored across several servers and data centers. If one server experiences an issue, another automatically steps in to serve the user without disruption.
This process is called data replication, which keeps all copies synchronized and up to date. It adds a layer of resiliency, reducing the chances of data loss and ensuring that businesses can continue to operate smoothly.
By spreading data across multiple servers, cloud platforms build a self-recovering network. Even during maintenance or technical failures, the system can instantly pull redundant data from another source, making downtime rare and helping businesses maintain continuous service.
For example, redundancy also supports faster disaster recovery. Since multiple data copies already exist in different locations, restoration becomes quick and efficient after a failure.
Some examples of major cloud providers include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS uses data replication across several availability zones. Hence, if one zone faces an outage, data remains safe and accessible from another.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Google Cloud automatically creates backups across regions, ensuring that even large-scale failures do not impact user access.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure’s geo-redundant storage (GRS) keeps data synchronized between two distant regions, offering maximum protection and faster recovery.
Each of these examples shows how global cloud providers rely on data redundancy to offer secure, always-available services.
By designing systems around redundant data, cloud platforms achieve high availability, smooth performance, and strong protection against failures. This innovative use of redundancy turns simple backups into a robust framework for reliability and user confidence.
Best Practices for Managing Data Redundancy
Managing data redundancy is all about finding the right balance to keep systems reliable without wasting resources. Businesses need strategies that maintain safety while controlling costs. With the proper structure and monitoring, redundant data can strengthen operations instead of slowing them down.
Let’s take a closer look at the best practices that organizations must consider when managing data redundancy.
Identifying necessary vs. excess redundancy
Not all redundancy is bad. The key is knowing which copies of data are essential and which are wasteful. Businesses should assess their systems through a risk-based evaluation, identifying the areas where data loss would be most damaging and focusing protection there.
For example, financial or customer data might require multiple backups, while temporary system logs might not. This selective approach helps reduce unnecessary duplication while maintaining reliability.
Using normalization and data governance
Normalization is a database design method that efficiently organizes data to avoid repetition. It ensures that each piece of information is stored only once and that all relationships are clearly defined. This helps minimize redundant data without compromising accessibility.
Strong data governance supports this process. It involves setting rules for how data is collected, updated, and stored. Clear policies keep information consistent and reliable across all systems. By combining normalization and governance, organizations can manage data redundancy effectively and keep databases clean.
Monitoring synchronization and version control
Even with careful planning, redundancy can create challenges if not tracked properly. Monitoring systems in real time helps businesses identify when data versions fall out of sync. Regular audits ensure that redundant data remains accurate and up to date.
Modern tools can automate this process. For instance, synchronization software and version control systems alert teams when changes occur or when data fails to replicate correctly. These tools make it easier to maintain a balance between reliability and efficiency while preventing minor sync issues from turning into bigger problems.
The goal is not to obliterate redundancy but to use it where it adds value. By combining smart planning, structure, and real-time monitoring, businesses can make their data systems safe and efficient.
Conclusion
Data redundancy is both a strength and a challenge in modern systems. When managed correctly, it protects critical information, prevents downtime, and improves reliability. If left unchecked, too much redundant data can raise costs, slow performance, and create confusion across systems.
The key lies in balance, where businesses must find the middle ground between reliability and efficiency. Investing in strong data management strategies, smart monitoring tools, and thoughtful system design ensures that redundancy serves as protection rather than a problem.
Partnering with the best app development firms for businesses building or upgrading digital systems can make all the difference. Experienced developers know how to design solutions that use redundancy wisely, enhancing reliability while keeping costs under control. Thus, smart redundancy is all about storing your data right.
Oct 16, 2025
