When choosing between TailwindCSS vs Bootstrap in 2026, we're really deciding between two fundamentally different approaches to web design. Bootstrap, created by Twitter developers in 2011, offers ready-made components that get you up and running quickly.
TailwindCSS, on the other hand, launched by Adam Wathan and Steve Schoger in 2017, provides low-level utility classes for building custom designs directly in your HTML.
The difference between Tailwind and Bootstrap goes far beyond their age. While Bootstrap includes everything needed for front-end development and powers sites for major organizations like NASA and Spotify, Tailwind focuses on generating CSS on-demand based on the utility classes you actually use.
This architectural difference has made Tailwind popular among teams working with a Website development agency that prioritizes performance, scalability, and long-term brand control.
This size difference is significant - Bootstrap weighs in at approximately 150KB compared to Tailwind's mere ~10KB, which directly impacts loading speeds. For teams debating bootstrap or tailwind, this performance consideration might be crucial.
In this tailwind css vs bootstrap comparison, we'll explore which framework better suits your specific project needs. We'll analyze their approaches to component reusability, brand consistency, and maintenance costs over time. By the end, you'll have a clear framework for making the right choice for your next web development project.
Tailwind vs Bootstrap: Key Differences

Comparison graphic showing Tailwind CSS and Bootstrap (https://www.material-tailwind.com)
The fundamental distinction between Bootstrap and Tailwind CSS lies in their core philosophies, which affect everything from design flexibility to maintainability. Let's explore these key differences to help you make an informed choice for your next project.
Component-first vs utility-first
The most significant difference between these frameworks is their underlying approach to styling. Bootstrap embraces a component-first philosophy, providing pre-built UI components like buttons, navbars, and forms with predefined styles. This approach focuses on layout consistency, making it ideal for projects that prioritize cohesive interfaces across multiple pages.
Tailwind CSS, conversely, follows a utility-first approach. Instead of pre-built components, it offers low-level utility classes that map directly to specific CSS properties. You combine classes like bg-blue-500, p-4, and text-center to build custom designs directly in your markup. This grants you pixel-perfect control without writing separate CSS files.
Opinionated UI vs brand-first UI
Bootstrap dictates a specific visual language with its structured, pre-designed components. While customizable through SASS variables, modifying Bootstrap's default styling often feels like fighting against the framework's baked-in design choices.
Tailwind is deliberately un-opinionated, functioning essentially as a powerful preprocessor for your own design system. Its configuration-based approach lets you define colors, spacing, typography, and breakpoints in a single tailwind.config.js file, making it ideal for projects requiring unique branding or custom design systems.
Rebrand mechanics: tokens vs overrides
When rebranding, Bootstrap requires you to modify SASS variables or build custom themes to override default styles. For example, changing your primary color means adding code like:
$theme-colors: (
"primary": #ff0000
);
Tailwind handles rebranding through its centralized configuration file, where design tokens become your single source of truth. This approach aligns perfectly with design systems, as tokens for colors, spacing, and typography scales can be updated in one place without fighting against pre-existing styles.
Styling workflow: where work happens
With Bootstrap, your HTML looks cleaner with fewer classes, but you'll often need additional CSS to modify default styles. This frequently involves context-switching between HTML and CSS files.
Tailwind keeps your styling within HTML markup through utility classes, eliminating the need to write separate CSS files. Though this creates longer class lists in HTML, many developers report faster development speeds after overcoming the initial learning curve.
Consistency ccontrol: prevent UI drift
Bootstrap excels at maintaining design consistency through its standardized components, especially beneficial for large teams or projects. Its structured approach creates a uniform look with minimal effort.
Tailwind requires more discipline to maintain consistency but offers superior flexibility through its configuration-driven approach. Teams using Tailwind effectively establish design tokens in the configuration file as guardrails against UI drift.
Governance: rules for brand consistency
Effective brand governance helps build a consistent brand experience across all touchpoints. Bootstrap's component library supports this with well-documented, pre-styled elements that enforce visual consistency.
Tailwind approaches governance differently, providing a framework where design tokens in the configuration file serve as the foundation for brand compliance. This centralized token system helps protect your brand's credibility by preventing the use of unauthorized colors, spacing, or typography.
Learning curve: team onboarding
Team onboarding speed matters during a rebrand, especially when multiple developers contribute to the UI. The learning curve of a CSS framework directly affects consistency, velocity, and how quickly new contributors can ship without breaking design rules.
Bootstrap offers a faster onboarding experience for most teams. Its extensive documentation, familiar component patterns, and predictable structure make it easy for new developers to start contributing immediately.
Engineers can rely on prebuilt components and established conventions, which reduces decision fatigue and lowers the risk of visual inconsistency. This makes Bootstrap a strong fit for teams that prioritize quick adoption and minimal training during a rebrand.
Tailwind CSS has a steeper onboarding curve. While the framework itself is simple, effective usage depends on utility fluency, shared conventions, and a clear component strategy.
New contributors must understand spacing scales, color tokens, responsive patterns, and when to extract reusable components. Without documented rules, Tailwind can lead to inconsistent utility usage and UI drift as more developers join.
In rebranding scenarios with many UI contributors, stricter standards become essential. Tailwind CSS requires upfront investment in documentation, component libraries, and usage guidelines to scale safely.
Bootstrap reduces this burden by enforcing structure through its component system, but at the cost of flexibility. The right choice depends on whether your team values faster onboarding or long-term design system control.
Reusability: how components scale
Bootstrap provides exceptional reusability through its extensive library of pre-built components. This approach is particularly valuable for rapid prototyping and projects with conventional interface requirements.
Tailwind promotes reusability through composition, encouraging developers to create reusable patterns with utility classes. Though initially more verbose, this approach ultimately leads to more maintainable, consistent codebases as projects grow.
Choose Bootstrap for Rebranding
Bootstrap stands out as an excellent choice for rebranding projects where speed, consistency, and established patterns are priorities. The framework's component-rich approach provides significant advantages when updating your brand's visual identity across web applications.
For teams facing tight deadlines, Bootstrap demonstrates remarkable efficiency. In one notable case study, a development team completed a radical rebrand in just two weeks by standardizing on Bootstrap.
This rapid turnaround was possible because they only needed to modify pre-existing Bootstrap styles in their framework rather than writing custom CSS from scratch. Furthermore, their adherence to reusing classes across the application enabled such quick implementation.
Bootstrap's extensive library of pre-designed components significantly accelerates the rebranding process. With over 12 million active websites using Bootstrap, the framework offers proven patterns that teams can customize rather than reinventing the wheel.
Additionally, its structured approach ensures visual consistency, a critical aspect of successful rebranding efforts.
Alongside its speed benefits, Bootstrap offers substantial customization flexibility. You can:
- Modify its CSS file to align with your brand guidelines
- Create a custom version via Bootstrap's customization page
- Leverage its expanded color palette with over 100 color options
- Utilize CSS custom properties as an alternative to SASS variables
Bootstrap 5's introduction of responsive font sizes further enhances its rebranding capabilities, automatically adjusting typography as viewport sizes change. Subsequently, this responsive approach extends to Bootstrap's 12-column grid system, ensuring your rebranded interface maintains its integrity across all devices.
When standardizing on Bootstrap for rebranding, teams often experience improved velocity and consistency. As one team discovered, using more Bootstrap classes and less custom CSS resulted in a significantly more consistent user experience across their application. Moreover, this approach reduced development effort for future features thanks to component reusability.
The framework's extensive community support proves invaluable during rebranding projects. With thousands of willing contributors on GitHub and abundant documentation, teams can quickly troubleshoot issues that arise during implementation.
Choose Tailwind CSS for Rebranding
Top CSS frameworks (Image Source)
Tailwind CSS emerges as the superior framework for rebranding projects that demand complete design freedom and pixel-perfect implementation of custom design systems. Unlike component libraries that require overriding default styles, Tailwind's utility-first approach provides a blank canvas for your brand's unique visual identity.
First and foremost, Tailwind excels in projects requiring granular control over every design element. Its configuration-driven approach allows you to define your brand's design tokens in a centralized file, creating a single source of truth for colors, typography, spacing, and other visual elements.
This token-based system aligns perfectly with modern design systems, enabling seamless collaboration between designers and developers.
For creative teams looking to break free from cookie-cutter designs, Tailwind's unopinionated nature is invaluable. As one design lead noted: "With Tailwind, we're not fighting against an existing design system, we're building our own." This flexibility allows for authentic expression of brand identity without the constraints imposed by pre-styled components.
Tailwind demonstrates considerable performance advantages in production environments. By generating only the CSS you actually use, Tailwind's output can be as little as 10kb after compression significantly smaller than Bootstrap's full package. Consequently, this leads to faster page loads and improved user experience metrics after rebranding.
The framework's approach to consistency differs fundamentally from Bootstrap's. Rather than enforcing consistency through pre-designed components, Tailwind establishes guardrails through its configuration:
- Design tokens in
tailwind.config.jsensure all team members use approved colors, fonts, and spacing - Custom plugins allow you to encapsulate complex design patterns as simple utility classes
- Composing utilities into component classes provides reusability without sacrificing flexibility
In fact, many teams report that Tailwind's utility-first approach actually improves long-term maintenance of rebranded interfaces. By eliminating the need for custom CSS overrides, Tailwind reduces technical debt and makes future brand refinements more straightforward.
Tailwind proves especially valuable for organizations embracing design systems built on atomic design principles. The framework's utility classes mirror the atomic approach, creating natural alignment between design thinking and implementation. This alignment often results in more faithful representation of design intentions in the final product.
In contrast to Bootstrap's approach, Tailwind offers superior support for incremental rebranding allowing teams to gradually implement brand changes without wholesale rebuilding of components. This capability makes Tailwind particularly well-suited for evolving brands that require ongoing refinement rather than one-time overhauls.
Decision Framework: Tailwind vs Bootstrap
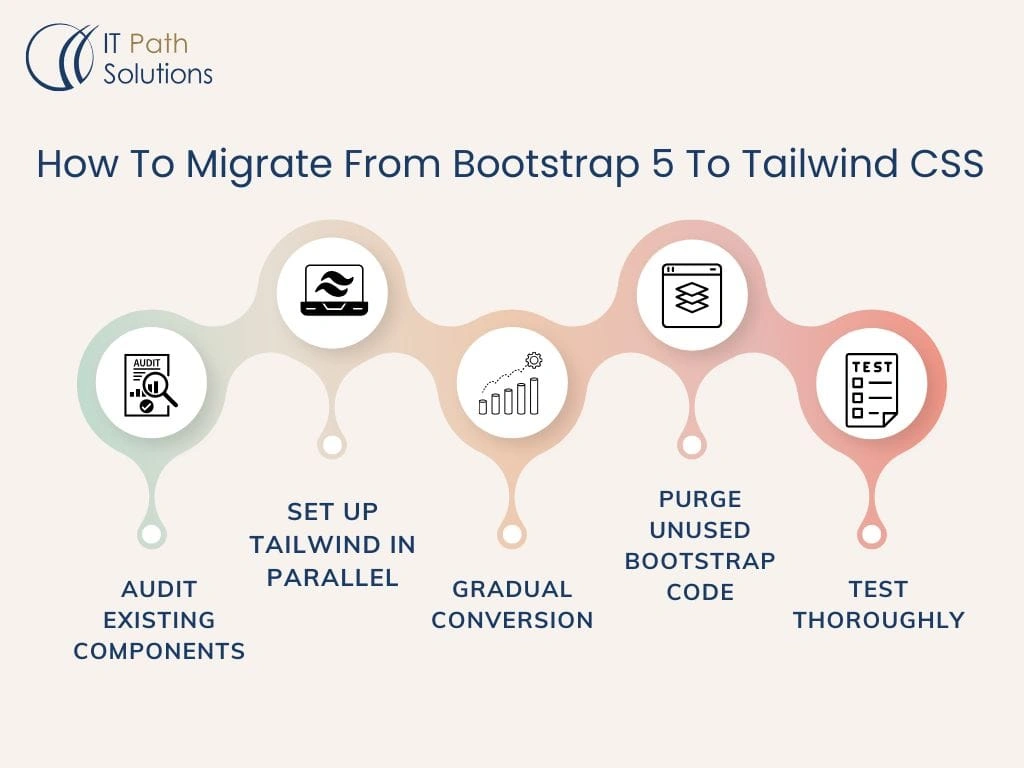
Step-by-step guide on migrating from Bootstrap 5 to Tailwind CSS (Image Source)
Selecting the optimal CSS framework involves weighing several critical factors that align with your project goals and team capabilities. This decision framework will help you systematically evaluate whether Tailwind CSS or Bootstrap best serves your specific needs.
Firstly, assess your project timeline and scope. If you're building a prototype or minimum viable product (MVP) with tight deadlines, Bootstrap's pre-built components offer immediate productivity gains.
Alternatively, for projects requiring unique branding and custom interfaces, Tailwind's utility-first approach provides superior flexibility despite an initially steeper learning curve.
According to industry adoption figures, over 42,000 companies currently use Bootstrap, compared to approximately 8,089 using Tailwind CSS. This disparity reflects Bootstrap's longer market presence and established reputation for enterprise applications.
When evaluating application type:
- Choose Bootstrap for corporate projects, internal tools, or standardized applications requiring professional consistency
- Select Tailwind for brand-focused sites, creative projects, or applications where visual differentiation is paramount
Team composition plays a decisive role as well. Bootstrap generally proves more accessible for beginners or full-stack developers who prefer ready-made solutions. Conversely, Tailwind rewards front-end specialists who understand CSS fundamentals and appreciate granular control.
Performance considerations might tip the scale toward Tailwind CSS, as its Just-In-Time compiler creates significantly smaller file sizes of approximately ~10KB compared to Bootstrap's ~150KB. This difference directly impacts page loading speed and user experience.
Even though both frameworks offer customization capabilities, your approach to design systems becomes the determining factor. Bootstrap excels at providing consistent interfaces through standardized components, whereas Tailwind enables pixel-perfect implementation of custom design systems through its configuration-driven methodology.
Interestingly, many successful teams don't view this as an either/or decision. As project requirements evolve, some organizations effectively combine both frameworks, using Bootstrap's structured components alongside Tailwind's utility classes for customization.
Prior to making your final decision, honestly evaluate your long-term maintenance needs. Bootstrap may accelerate initial development but could require extensive overrides as projects mature. Tailwind might demand more upfront investment but often proves more maintainable for evolving applications with unique design requirements.
Migration Playbook: Rebrand Implementation Steps
Implementing a rebrand between TailwindCSS and Bootstrap requires a systematic approach to ensure visual consistency throughout your application. The most effective strategy involves tackling the migration component by component, as attempting to convert an entire page at once can overwhelm both developers and AI tools.
To begin the migration process:
- Review your existing codebase thoroughly to identify corresponding components between frameworks
- Isolate specific components like navigation bars or hero sections before conversion
- Consider AI-powered converters for initial code transformation with approximately 90% accuracy
- Perform manual refinement for arbitrary values, shadows, and z-index properties that AI tools cannot perfectly translate
- Test extensively after conversion, targeting the largest breakpoints first before adjusting for smaller screens
Although some teams report spending approximately 30 hours on migration, others have completed radical rebrands in just two weeks by properly abstracting framework styles from the application. This efficiency becomes possible when developers consistently utilize framework classes and document any custom components.
A crucial caution: avoid mixing Tailwind and Bootstrap on the same page during transition phases, as their reset stylesheets conflict with each other, specifically regarding box-sizing and default margins. Additionally, be mindful that responsive breakpoint values differ slightly between frameworks, necessitating careful adjustment during implementation.
Conclusion: Bootstrap vs Tailwind Summary
Choosing between TailwindCSS and Bootstrap ultimately depends on your specific project requirements, team expertise, and design goals. Both frameworks offer distinct advantages that make them suitable for different scenarios.
Bootstrap shines when rapid development and consistency are priorities. The component-first approach allows teams to build professional-looking interfaces quickly, especially for corporate applications or projects with tight deadlines. Additionally, Bootstrap's extensive community support and documentation provide valuable resources for troubleshooting and implementation.
Tailwind CSS, however, excels in projects demanding unique branding and pixel-perfect design implementation. The utility-first methodology grants developers granular control over every visual element while maintaining performance benefits through significantly smaller file sizes.
Undoubtedly, this approach proves more maintainable long-term as projects evolve beyond initial implementation.
Team composition also plays a crucial role in this decision. Bootstrap generally works better for beginners or full-stack developers preferring ready-made solutions, whereas Tailwind rewards those who understand CSS fundamentals and value detailed customization.
The framework you select today will shape your development workflow, maintenance costs, and brand consistency for years to come. Therefore, carefully evaluate your project timeline, application type, team capabilities, and performance requirements before making your choice.
Though presented as competitors, many successful teams don't view this as an either/or decision. Some organizations effectively combine both frameworks, leveraging Bootstrap's structured components alongside Tailwind's utility classes for customization.
Whichever framework you choose, remember that both TailwindCSS and Bootstrap have earned their places in modern web development for good reasons. Your decision should align with your specific project needs rather than following trends. The best framework is simply the one that helps your team deliver exceptional user experiences most effectively.
Feb 4, 2026
