Design is critical in shaping how we interact with information and consume knowledge. Whether in statistical charts and posters or mobile applications and digital products, good designs help understand the content and makes the experience enjoyable.
The rising importance of design and visual communication has increased the popularity of two areas working closely on these aspects: graphic design and UI/UX design. Both graphic design and UI/UX design focus on the visual elements and how information is presented. However, while graphic design concentrates more on aesthetics, UI/UX design prioritizes usability and interaction.
The differences between graphic design and UI design can be a bit difficult to understand. However, it is important for designers to be aware of the different approaches and purposes of graphic design, UX design, and UI design.
In this article, we compare the two creative processes of graphic design and UI/UX design. We will cover the basics of both disciplines and then provide an in-depth comparison, focusing on graphic design vs UI/UX design.
Read along as we highlight the key differences between these two highly popular work areas.
Defining Graphic Design

Graphic design, a field that has existed for some time, deals with the creation and production of visual content to make information accessible and understandable.
Graphic design is the creation of visuals to communicate ideas and deliver messages. Designs include both print and digital elements, with the help of elements such as typography and imagery. The primary goals of graphic design and designers include sharing information, persuading the audience, and increasing engagement.
Some standard outputs of graphic design are as follows.
- Posters: Designed to deliver specific messages in an engaging and captivating manner
- Logos: A part of a brand’s visual identity that becomes its symbol
- Brand identities: A comprehensive visual system that defines the brand’s overall look and feel
- Typography: The design and use of written content to enhance meaning and aesthetics Social media graphics: The visual content that is shared across social media platforms

Good graphic design skills are critical for any modern organization. Graphic designers, owing to the content they produce and the persuasion that visuals offer, contribute to building an organization's strong visual identity, which can lead to trust in the brand. Additionally, graphic design improves clarity in communication while leveraging emotional elements.
Tools Used by Graphic Designers
Graphic design focuses on efficiently delivering information while considering aesthetics and visual impact. Graphic designers use several tools to help them perform their work effectively. Some important ones are as follows.
Adobe Photoshop
Adobe Photoshop is ideal for editing photos and creating engaging digital artwork. It is widely used for creating social media visuals, editing high-quality images, and producing graphics for the web.
Adobe Illustrator
Adobe Illustrator is an excellent tool for creating vector graphics, particularly logos, icons, and illustrations. This tool can come in handy when creating brand identities and visual components that need to be scaled without compromising the quality.
Adobe InDesign
Graphic designers use Adobe InDesign to create documents such as magazines, brochures, and posters. This tool offers excellent control over typography and allows designers to present information creatively.
Canva
Canva is a tool for graphic designers. Its simple drag-and-drop features can help aspiring designers and beginners create templates, visuals, and documents.
Defining UI/UX Design

User interface (UI) design involves creating visual and interactive elements, particularly in digital products. These elements, such as buttons, menus, and layouts, shape how users interact with a design while focusing on the overall look and feel.
On the other hand, user experience (UX) design is more about the entire user experience and journey as they interact with a product or service. In this case, the overall goal is to ensure the users have a satisfying experience when interacting with the design.
Owing to the similarity of design principles, the value of interactive design, the overlap in the work, and the expertise required by professionals, UI and UX design are often collectively referred to as UI/UX design.In practice, this crossover often leads product teams to work alongside a UI design services company, especially when scaling design systems or refining complex interaction patterns that require dedicated expertise. However, it is essential to understand the difference between these closely related fields.
User interface design focuses on visual elements, such as buttons, icons, visual hierarchy, and color themes. User experience design is more concerned with the overall experience, i.e., how users navigate a design and accomplish their tasks.
For example, in the case of websites, UI design aspects would determine the visual appeal and accessibility of the designs, while UX would ensure users can find information easily. Similarly, when considering a SaaS platform, UI typically focuses on organizing dashboards and controls, while UX prioritizes optimizing workflows.
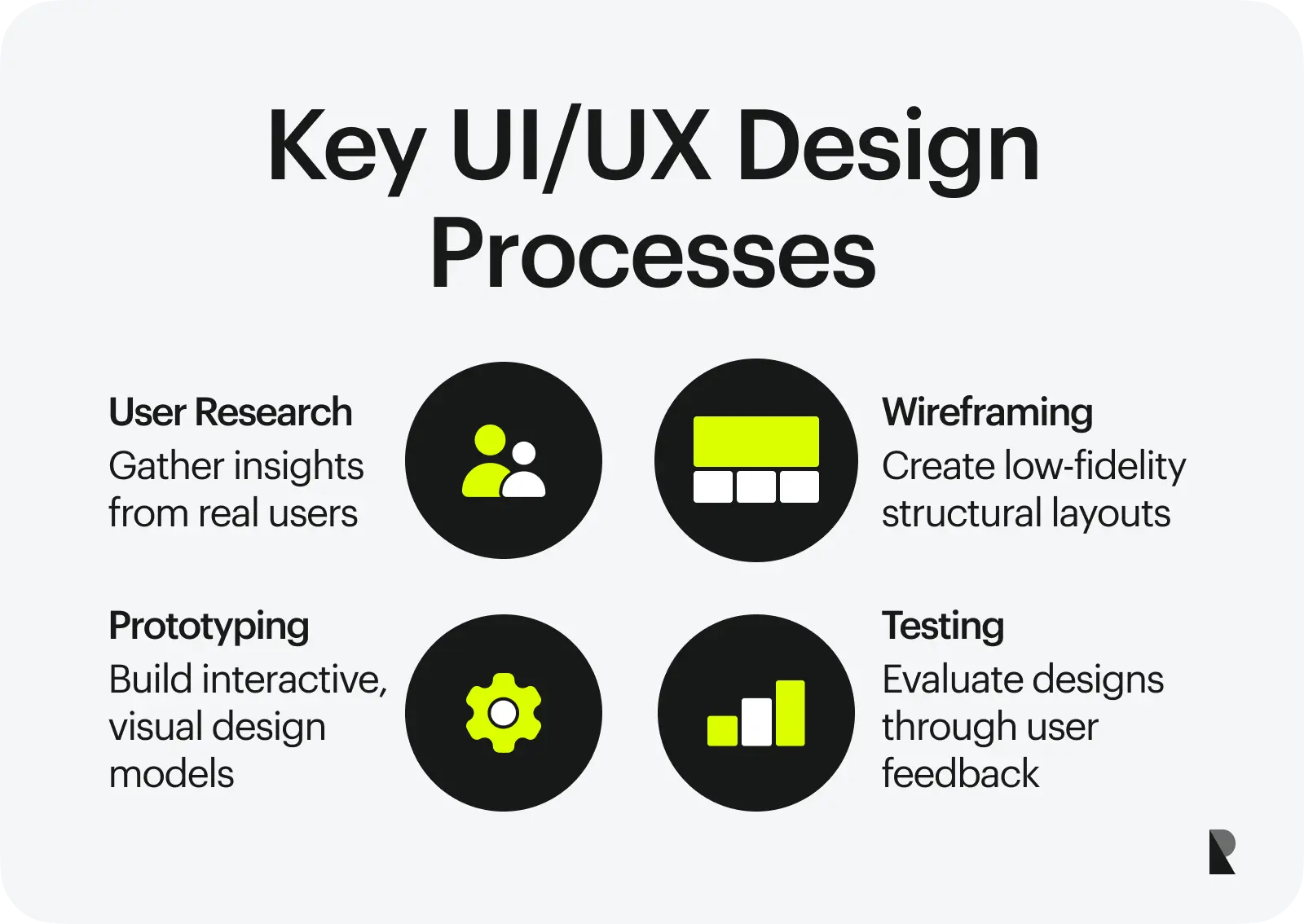
Important UI/UX Design Processes
Designing interactive and engaging user interfaces is a strategic technique that relies on key design principles and critical design processes. Some essential design processes in UI/UX design are as follows.
User research
User interface and user experience design draw heavily from user research and feedback from real users. This is the phase where designers gather insights into user behavior, attitude, and pain points to better understand their needs. Any UI/UX design agency hiring a new designer would require traits such as empathy and skills such as interviewing from an aspiring professional.
Wireframing
Wireframing is a critical UI/UX design process where designers create simple, low-fidelity product or service layouts. The focus in this process is not on the aesthetics but on creating a functional skeleton of the design.
Prototyping
A key process in UI/UX design is prototyping, where designers use wireframes and add visual elements to them. They also build interactions between different elements in a design and simulate the user journey.
Testing
UI/UX design is an iterative process in which evaluation and assessment provide valuable data for development and improvement. Designers conduct various tests, such as usability studies and A/B testing, to highlight users' pain points and develop the design further.
Tools Used by UI/UX Designers
Similar to graphic design, UI/UX designers have several important tools at their disposal. These tools not only make their work easier but also help in collaboration and streamlining the processes. Some important UI/UX design tools are as follows.
Figma
Figma is an excellent design tool that allows designers to collaborate in real-time. This tool is ideal for creating early prototypes and designs, especially when working in design teams.
Sketch
Sketch is an important tool used by UI/UX designers. It focuses mainly on vector elements and helps create a library of UI components, particularly when the reuse of design elements is a key goal.
AdobeXD
Adobe XD is a sophisticated tool that helps design UI elements and create interactive prototypes. This tool integrates well with other Adobe tools, thus allowing UI/UX designers to collaborate with graphic designers.\
InVision
InVision is typically used by designers to create prototypes from static screens. The simplicity of this tool helps generate interactive versions of early-stage prototypes, thus creating designs that can be tested easily.
Key Differences Between Graphic Design and UI/UX Design
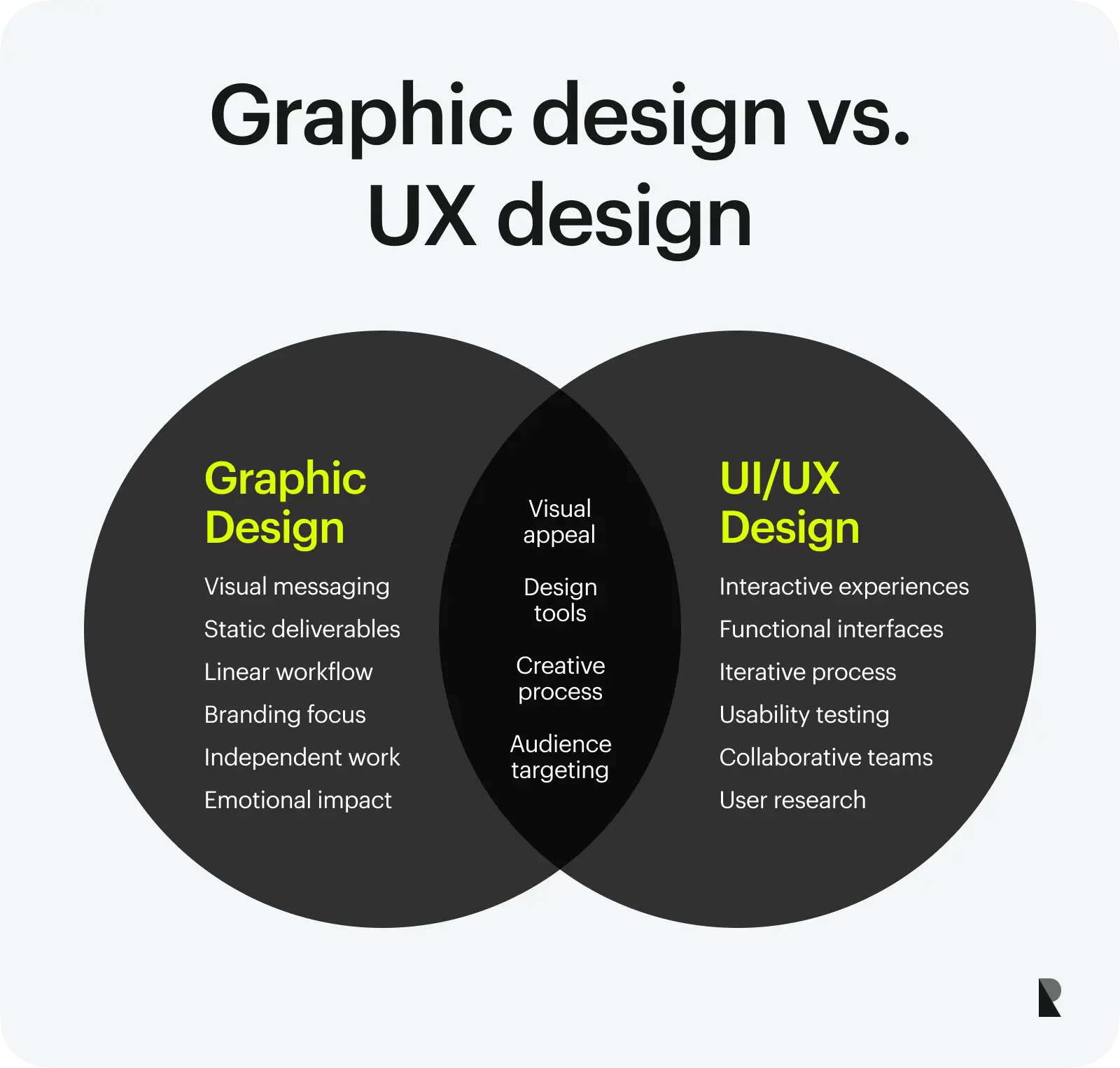
Now that we’ve established a basic understanding of graphic and UI design, let us compare both fields by focusing on some key aspects that highlight their differences.
The table below summarizes graphic design vs UI/UX design.
| Aspect | Graphic design | UI/UX design |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Deliver effective messages in a visual manner | Create interactive, functional, and satisfying experiences |
| Methods | Typography, visual hierarchy, branding principles, and layout | User research, wireframing, prototyping, and user testing |
| Design goals and end users | Visual appeal for the target audience, focusing on brand identity | Easy-to-use interfaces that help users achieve their goals |
| Tools and technologies used | Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign, Canva, etc. | Figma, Sketch, Adobe XD, InVision, etc. |
| Workflow and processes | Mostly linear: brief → concept → execution | Iterative: research → prototype → test → refine |
| Collaboration and teams | Typically independent or with marketing teams | Collaboration with developers, product managers, etc. |
| Output and deliverables | Static visuals, such as posters, logos, brand identity, etc. | Interactive interfaces, prototypes, design systems, etc. |
| Metrics of success | Visual appeal and emotional impact | Usability test results, conversion rates, user retention, etc. |
Let us take a closer look at some of these aspects.
Design goals and end users
Graphic design focuses on producing creative visuals that deliver a strong message with an attractive layout. Designers usually rely on media such as posters, infographics, and advertisements to create a strong brand identity.
On the other hand, UI design is about shaping the entire user experience as they interact with a product or service. Some essential aspects of good UI/UX design include improved functionality, better navigation, and a smooth experience.
Let’s take the example of a health or fitness mobile application. A graphic designer might focus on an eye-catching poster that promotes the app and conveys the overall message, while a UI/UX designer would focus on the app's design.
Tools and technologies used
As discussed above, the tools and technologies used in graphic and UI design vary greatly. Graphic design uses tools such as Photoshop and Illustrator to create quality visuals. UI/UX design, on the other hand, relies more on tools such as Figma and Adobe XD to create wireframes and interactive prototypes.

Tools for Graphic Design and UI/UX Design (Image Source)
However, there can be some overlap in the tools used in graphic and UI design, as both fields prioritize visual appeal. For example, UI/UX designers can sometimes use Photoshop and Illustrator to create some design elements.
Workflow and process
The workflow of graphic design vs. UI/UX design is significantly different. Graphic designers usually follow a linear trajectory in their workflow, starting from a clear brief. This brief leads to the development of a concept, which then leads to the execution, which creates the artifact.
UI designers, on the other hand, follow an iterative approach. The process begins with user research, which helps them better understand users’ needs. This information helps create wireframes and interactive prototypes, which are then tested. The test results and feedback from users then help refine the design and create an improved iteration.
Collaboration and team involvement
Graphic and UI design disciplines also vary in their approaches to teamwork and collaboration. While graphic designers usually work independently, UI/UX designers work more collaboratively.
Sometimes graphic design requires working with marketing or branding teams; however, this is not the norm. Working with developers, product managers, and analysts is part of the process for UI design.
Output and deliverables
Another aspect where graphic design and UI design differ is the nature and type of output they deliver. Graphic designers typically create static visuals, such as branding materials, logos, posters, and infographics. These designs need to be visually appealing and engaging for the target audience.
UI/UX designers, on the other hand, create dynamic products and services, such as prototypes, websites, and mobile applications. Most of the top UX design agencies focus on delivering these outputs along with refined versions of prototypes after assessment, which leads to improved designs.
Metrics of success
When we compare UI/UX to graphic design, another key area of comparison is the metrics of success. In the case of graphic design, success is measured by the visual appeal and emotional impact of the design. These elements contribute to the brand image and visibility, highlighting how well design can support branding and marketing efforts.
In the case of UI design, success is linked to user engagement and conversion rates. UI/UX design measures user satisfaction with a product or service and the usability scores that impact the overall experience.
Conclusion
Graphic design and UI/UX design are both visual and creative disciplines that produce interactive and engaging content. However, their purposes, processes, and outcomes differ greatly. While graphic design focuses on visual storytelling, UI/UX design prioritizes user interaction with designs.
Both disciplines are critical for modern organizations, particularly those focusing on creating a strong digital presence. If you’re an aspiring designer considering choosing between graphic design and UI design for your career, the first step is to know your interests and skill set.
Graphic design may be the right fit if you’re drawn to artistic impression and branding. On the other hand, if you’re more interested in shaping user journeys and solving complex design problems, UI/UX design might be a better path.
This article provides an overview of both disciplines, providing the basic understanding you need to explore them in depth and find what works best for you.
Jul 9, 2025
