
Graphical user interfaces (GUIs) have become the norm in interacting with digital products and services. From handheld devices to desktop computers and virtual reality experiences, GUIs help users make sense of complicated information. Using icons, buttons, and text elements, GUIs help create user-friendly designs.
The quality of graphical user interfaces can be the deciding factor in the success of a product and, by extension, a business. Products with better, efficient, and understandable GUIs automatically gain a competitive advantage in the market.
Because of that, many teams should turn to an experienced UI & UX design company to translate complex systems into clear, intuitive interfaces. Working with specialists who understand both interface behavior and visual communication helps ensure that the product feels approachable to users, scales well across platforms, and supports real business goals rather than just looking polished on the surface.
In this article, we focus on graphical user interfaces (GUIs). We start by providing an overview of the concept and history of GUIs. We then discuss the key principles and applications of GUIs and some practical examples.
Read along as we explore this fascinating concept and highlight its significance for modern UI/UX designers and agencies.
Defining Graphical User Interface (GUI)?
A graphical user interface (GUI) is, in fact, a visual layer of a digital product or service. By replacing complex commands and backend design elements with icons, buttons, and visuals, GUIs allow users to interact with designs easily and understandably.

GUIs are of immense importance in UI/UX design as they quite literally define how users interact with a digital product. Good, accessible GUIs are intuitive, familiar, and user-friendly, thus making the lives of the target audience easier.
Some core components of GUIs include icons, buttons, windows, and menus. Icons serve as visual cues, thus representing actions and objects on the screen. Buttons are essential as most digital interactions happen through interactive, clickable buttons. Windows provide a space where users can see all the GUI elements. Menus are necessary to organize and present the information logically. Together, these core elements help users make sense of information and navigate through digital environments.
Compared to command-line interfaces (CLIs), GUIs provide a more interactive experience. Where the former requires users to type in instructions, the latter uses point-and-click, drag-and-drop, and other simple gestures, thus making the interactions more fulfilling and simplifying digital interactions. With the help of efficient GUIs, one does not have to be an expert to interact with digital products and services.
Brief history of GUI evolution
Graphical user interfaces (GUIs) are not a new concept in design. Instead, they have undergone advancements, changes, and innovations over the last few decades. Key innovators like Douglas Engelbart from Xerox PARC and Steve Jobs played vital roles in advancing GUI technology.
An Old Graphical User Interface (Image Source)
The first GUI was developed at Xerox PARC back in the 1970s. This early GUI concept introduced windows, icons, and mouse-based interfaces. In 1984, Apple released the Macintosh, bringing the GUI idea closer to the consumer market. This move was a significant turning point in the development of GUIs, as individuals could now use these interactive interfaces for personal computing. This later led to the introduction of operating systems such as Microsoft Windows and Apple OS.
More recent developments in GUIs have come from touchscreen and mobile interfaces. With Android and iOS, GUIs are moving away from mouse-based interfaces and creating more interactive user experiences. Additionally, with new technologies, such as augmented and virtual reality, gestures and motions are now taking over GUIs, thus adding another layer of interactivity.
Why GUI Matters?
Graphical user interfaces (GUIs) must not be misunderstood as just visual and aesthetic elements of digital products and services. They significantly impact the overall user experience, levels of interactivity, and user satisfaction. Additionally, well-designed GUIs make businesses more trustworthy, thus increasing brand loyalty.
A clean, intuitive GUI helps users find the correct information quickly and easily, making tasks easier to complete. All modern businesses, aiming for success and a competitive edge, put significant effort into building interfaces.
GUIs also play an essential role in improving the accessibility and localization of a digital design. For example, visual cues and icons help users from different backgrounds relate to the content and achieve their goals. Similarly, replacing complex text commands with buttons and gestures helps reach a broader audience.
GUIs offer clear advantages for developers and product designers. They allow for faster product adoption, increase user engagement, and help design a consistent experience across different platforms and devices.
Key Principles of Effective GUI Design
Now that we know the significance of quality graphical user interfaces in enhancing the user experience, it is essential to highlight some key principles of GUI design. When designing an effective GUI, an important goal is to ensure that it presents information in a simple way, making it findable and valuable simultaneously.
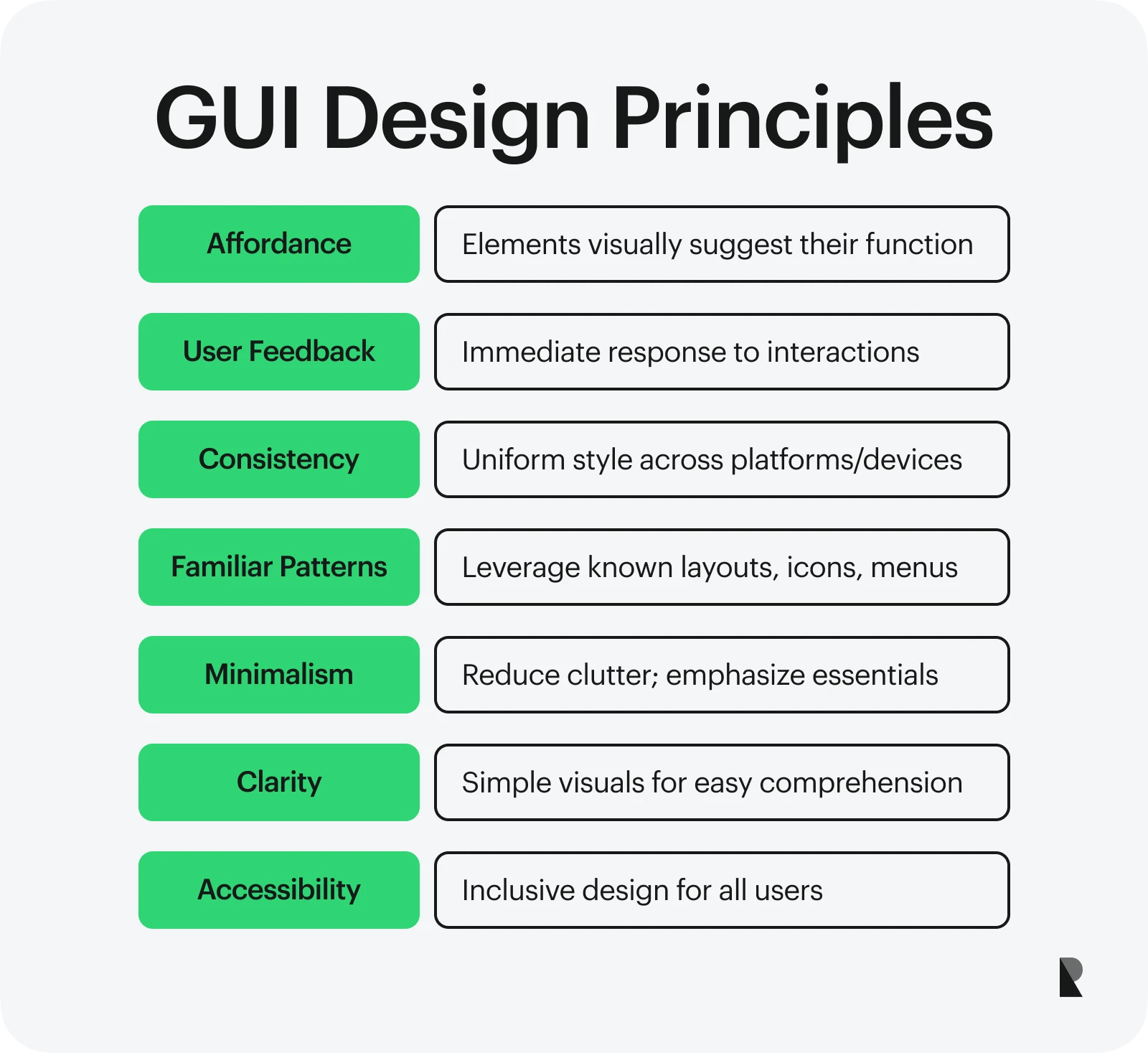
Any UI/UX design agency values a good understanding of GUI design principles when hiring a new designer. Some essential principles are discussed below.
Affordance & user feedback
Like any UI/UX design project, affordances are essential when designing graphical user interfaces. Interface elements like buttons, icons, and visuals should suggest their purpose. This means that buttons should stand out and look clickable, and sliders should appear as if they can be dragged. These visual cues are equally crucial for text interfaces, as some aspects (such as buttons and visual hierarchy) are also present there.
Designers must also ensure users get quick feedback when interacting with a GUI. Whether it is a task as small as clicking a button or as complicated as file management, users prefer instant results to know whether they’re getting closer to their goals. Therefore, exemplary GUIs should be valued and designed to meet this need.
Consistency & familiar patterns
Consistency is another essential principle when designing helpful and user-friendly interfaces. Consistency has recently become more critical when a business has to maintain its presence on multiple platforms and ensure that users from different mobile devices, web browsers, and operating systems can access the same design.
Additionally, users rely on familiar design patterns, such as navigation, colors, layout, and hamburger menus. Designers must adhere to certain conventions and design components to reduce users’ cognitive load. A consistent and familiar GUI operating on multiple platforms builds trust and helps users achieve their goals.
Minimalism & clarity
It is believed that for a good design, less is often more. This means that a good design can address the needs of its target audience with a minimalist approach. When designing a GUI, the visual design and the choice of design elements should be such that they avoid clutter and bring clarity to the interface.
Like the familiarity principle, a minimalist design reduces cognitive load and prevents users from being overwhelmed. A clean and simple design ensures that users focus on the essential parts of an interface and initiate an action that contributes to their overall goal.
Accessibility best practices
When designing a GUI, accessibility can never be ignored, particularly regarding digital designs and web-based interfaces. Designers should always ensure that the visual elements in the interface have a good contrast and that the graphical elements do not hinder users with disabilities.
GUIs can be made accessible by incorporating alternative modes of interaction, such as integrating voice commands for text-based interfaces, ensuring support for character user interfaces, and supporting screen readers. It is also important to note that creating accessible designs is ethical and inclusive, meets legal standards, and expands a product's overall reach.
GUI Applications Across Industries
Graphical user interfaces (GUIs) are used in various industries, helping users navigate complex systems, understand complicated information, and simplify their tasks. A user-friendly GUI, whether in touch screen or mouse-based interfaces, adapts to users' needs and enables quick decisions, thus bringing efficiency to task management.
Some key examples of industries where user interface, GUI, and user experience come together are as follows.
E-Commerce
Software applications with efficient GUIs streamline user experience in online shopping, marketing, and retail services. Essential features like product preview, one-click checkouts, and comparison help increase conversion rates.
Healthcare
Healthcare is another area where GUI has vast applications. Medical software with clear and intuitive dashboards allows quick access to patient records, lab results, and other helpful tools, thus simplifying care delivery.
GUI in the Healthcare Industry (Image Source)
Gaming
GUIs are essential in delivering a quality gaming experience. Quick access to settings, menus, and in-game options, such as character health indicators, helps create an immersive experience for players and contributes to a game's success.
Education
The online and digital environment has impacted the education industry like any other field. With online certifications and massive open online courses (MOOCs), it has become essential to deliver quality digital experiences. Sound GUI design principles can help students track their progress, accomplish tasks, and improve the learning experience.
When organizations hire UI design companies, they examine their portfolios closely, seeking examples from different industries. Therefore, it is essential to understand the nuances of GUI design and its various applications.
Tools & Frameworks for GUI Development
Designers need the tools, skills, and frameworks to build effective graphical user interfaces. Designers and developers need several essential resources to create user-friendly interfaces across desktop, web, and mobile platforms.
Popular tools for GUI development
GUI development tools help streamline the overall process of designing and prototyping user interfaces. GUI development tools help in all stages of design, particularly when it comes to wireframing, prototyping, and user testing.
What are some popular tools for GUI development?
Some popular tools for GUI development are as follows. 1. Figma 2. Adobe XD 3. Sketch 4. InVision 5. Axure RP
Some important examples of GUI development tools are listed below.
Figma
Figma is a cloud-based design tool that is quite popular among designers. Its simple, intuitive interface and collaboration features make it a desirable tool for professionals working on GUI design and development.
Figma is beneficial in creating early prototypes of GUIs. It allows designers to incorporate interactive features and develop a comprehensive prototype for evaluation.
Adobe XD
Adobe XD is another helpful tool for GUI development. Similar to Figma, Adobe XD can help create initial prototypes. However, this tool supports vector design and interactive transitions, assisting designers in creating slightly complex mockups and user flows.
One of Adobe XD's strongest features is its easy integration with other Adobe tools, such as Photoshop and Illustrator. Designers and developers who are comfortable with the Adobe suite find it easy to work with Adobe XD.
Sketch
Sketch is a macOS GUI development tool popular among designers because of its simplicity. This tool creates early, static versions of website and mobile application prototypes.
Sketch for GUI Development (Image Source)
Unlike Figma, Sketch is not a browser-based application. However, it integrates well with other tools, such as Zeplin, leading to design handoff. Sketch also has several helpful plugins, making it a favorable choice for designers.
InVision
InVision is primarily known for developing interactive prototypes quickly and effectively. This tool is also known for its support for collaboration, creating an environment where designers and developers can work together and see the design through several critical stages.
InVision allows designers to create static designs and simulate complex user flows. Additionally, InVision helps with the iterative nature of GUI development by supporting user testing and feedback collection.
Axure RP
Axure RP is an advanced tool for GUI development primarily used to create complex, data-driven interfaces. Experienced developers and designers generally use it to build highly functional prototypes without writing code.
Axure RP is favored by designers who build interactive, logic-based prototypes with dynamic content and complicated workflows. This tool also includes a built-in documentation feature that simplifies the handoff process.
Useful frameworks for GUI development
Along with tools used to develop effective graphical user interfaces, designers and developers also need to understand and utilize essential frameworks. GUI development frameworks provide a foundation and structure for building efficient and interactive interfaces. These frameworks have design elements, components, and libraries that help create a consistent design environment.
What are some useful frameworks for GUI development?
Some practical frameworks for GUI development are as follows. 1. React 2. Flutter 3. Qt 4. Electron
Some important frameworks for user interface, GUI, and prototype development are as follows.
React
React is a JavaScript library for developing user interfaces, particularly web applications. Meta developed React, which is now an open-source library widely used by GUI developers.
This framework is ideal for cases where design teams must create and manage reusable UI components over time. React's flexibility allows designers to use the library components in multiple projects, thus adding to its utility.
Flutter
Flutter is another practical framework for GUI designers and developers. Google maintains this software development kit (SDK). It serves as a valuable toolkit for creating interactive prototypes, particularly when designers create native mobile and web applications.
Flutter’s strength lies in its efficiency and how it helps developers create consistent applications with smooth interactions.
Qt
Qt is an advanced GUI development framework for designing desktop applications. It supports several operating systems, including macOS, Windows, and Linux.
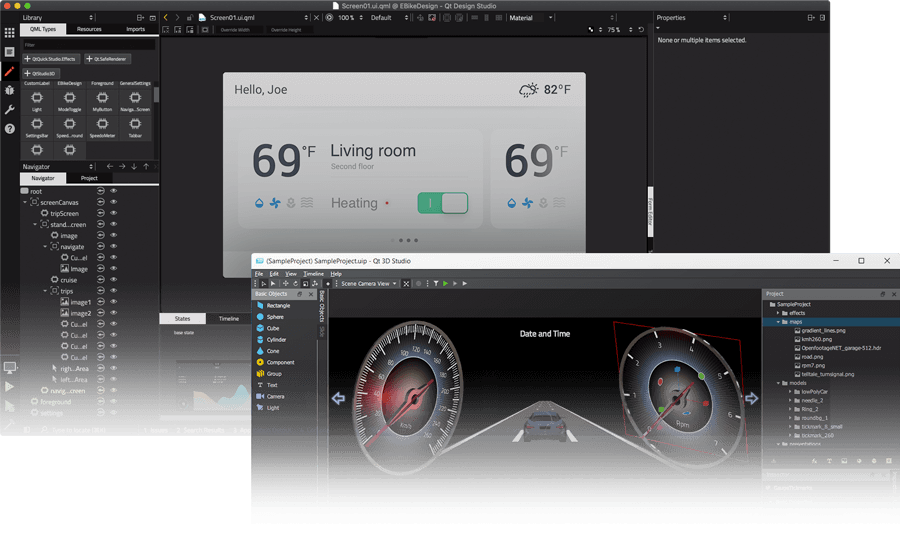
Qt as a Framework for GUI Development (Image Source)
This framework is popular because of its comprehensive set of UI components and tools that can help designers build native, responsive, and highly interactive designs with dynamic content.
Electron
Electron is another popular GUI development framework. It is used to build cross-platform desktop and web applications that integrate HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Electron works well for teams with specific expertise and familiarity with web development who want to develop a consistent desktop experience.
Conclusion
Graphical user interfaces (GUIs) are visual gateways or bridges that help users achieve their goals in the highly saturated digital environment. GUIs make technology accessible by translating the complicated backend commands to interactive, user-friendly elements with the help of buttons, icons, and visuals.
GUI design and development have seen a lot of innovation with the advancement of technology. In the years to come, the popularity and significance of GUI design will only increase in the industry as it helps shape user experiences in almost every discipline.
The rising demand for GUI in the industry requires that all aspiring designers understand the key principles of UI/UX design, focus on users’ needs, and gain expertise in essential GUI design tools and frameworks.
Aug 19, 2025
